Radiographic results of single level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative lumbar spine disease: focusing on changes of segmental lordosis in fusion segment
- PMID: 19956478
- PMCID: PMC2784961
- DOI: 10.4055/cios.2009.1.4.207
Radiographic results of single level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative lumbar spine disease: focusing on changes of segmental lordosis in fusion segment
Abstract
Background: To assess the radiographic results in patients who underwent transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), particularly the changes in segmental lordosis in the fusion segment, whole lumbar lordosis and disc height.
Methods: Twenty six cases of single-level TLIF in degenerative lumbar diseases were analyzed. The changes in segmental lordosis, whole lumbar lordosis, and disc height were evaluated before surgery, after surgery and at the final follow-up.
Results: The segmental lordosis increased significantly after surgery but decreased at the final follow-up. Compared to the preoperative values, the segmental lordosis did not change significantly at the final follow-up. Whole lumbar lordosis at the final follow-up was significantly higher than the preoperative values. The disc height was significantly higher in after surgery than before surgery (p = 0.000) and the disc height alter surgery and at the final follow-up was similar.
Conclusions: When performing TLIF, careful surgical techniques and attention are needed to restore and maintain the segmental lordosis at the fusion level.
Keywords: Lumbar osteoarthritis; Segmental lordosis; Spinal fusion; Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.
Figures


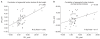
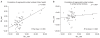
References
-
- Harms JG, Jeszensky D. The unilateral, transforaminal approach for posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Orthop Traumatol. 1998;6(2):88–99.
-
- Hee HT, Castro FP, Jr, Majd ME, Holt RT, Myers L. Anterior/posterior lumbar fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: analysis of complications and predictive factors. J Spinal Disord. 2001;14(6):533–540. - PubMed
-
- Humphreys SC, Hodges SD, Patwardhan AG, Eck JC, Murphy RB, Covington LA. Comparison of posterior and transforaminal approaches to lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26(5):567–571. - PubMed
-
- Lim HJ, Kwon SC, Roh SW, Jeon SR, Rhim SC. Outcomes of unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative lumbar spine disease. Korean J Spine. 2005;2(1):19–25.
-
- Potter BK, Freedman BA, Verwiebe EG, Hall JM, Polly DW, Jr, Kuklo TR. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: clinical and radiographic results and complications in 100 consecutive patients. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(4):337–346. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

