A preliminary results of a randomized trial comparing monthly 5-flourouracil and cisplatin to weekly cisplatin alone combined with concurrent radiotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer
- PMID: 19956508
- PMCID: PMC2785420
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2005.37.1.37
A preliminary results of a randomized trial comparing monthly 5-flourouracil and cisplatin to weekly cisplatin alone combined with concurrent radiotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the superior chemotherapeutic regimen between monthly 5-FU plus cisplatin (FP) and weekly cisplatin alone in concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer, the compliance of treatment, response, survival and toxicities were analyzed between the two arms.
Materials and methods: Between March 1998 and December 2001, 61 patients with locally advanced cervical cancer (stage IIB through IVA) and negative para-aortic lymph nodes were randomly assigned to either 'monthly FP' (arm I, n=34) or 'weekly cisplatin' (arm II, n=27) with concurrent radiotherapy. The patients of arm I received FP (5-FU 1,000 mg/m(2)/day + cisplatin 20 mg/m(2)/day, for 5 days, for 3 cycles at 4 week intervals) and those of arm II received cisplatin (30 mg/m(2)/day, for 6 cycles at 1 week intervals) with concurrent radiotherapy. The radiotherapy consisted of 41.4 approximately 50.4 Gy external beam irradiation in 23 approximately 28 fractions to the whole pelvis, with high dose rate brachytherapy delivering a dose of 30 approximately 35 Gy in 6 approximately 7 fractions to point A. During the brachytherapy, a parametrial boost was delivered. The median follow-up period for survivors was 44 months.
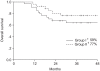
Results: The compliance of treatment in monthly FP weekly cisplatin arms were 62 and 81%, respectively. The complete response rates at 3 months were 96 and 88% in arms I and II, respectively. The 4-year overall survival and disease free survival rates were 64 and 54% in the arm I and 77 and 66% in the arm II, respectively. The incidence of hematologic toxicity more than grade 2 was 29% in the arm I and 15% in the arm II. Only one patient in arm I experienced grade 3 gastrointestinal toxicity. No severe genitourinary toxicity was observed.
Conclusion: No significant difference was observed in the compliance, responses, survival rates and acute toxicities between the two treatment arms. More patients and further follow up will be required.
Keywords: Cervical neoplasm; Concurrent chemoradiotherapy; Randomized trials.
Figures


References
-
- Gonzalez DG, Ketting BW, Bunningen BV, Dijk JD. Carcinoma of the uterine cervix stage IB and IIA: result of postoperative irradiation in patients with microscopic infiltration in the parametrium and/or lymph node metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989;16:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Coia L, Won M, Lanciano R, Marcial VA, Martz K, Hanks G. The patterns of care outcome study for cancer of the uterine cancer: Results of the second national practice survey. Cancer. 1990;66:2451–2456. - PubMed
-
- Jampolis S, Andras EJ, Fletcher GH. Analysis of sites and causes of failures of irradiation in invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the intact uterine cervix. Radiology. 1975;115:681–685. - PubMed
-
- Leibel S, Bauer M, Wasserman T, Marcial V, Rotman M, Hornback N, et al. Radiotherapy with or without misonidazole in patients with stage IIIB or IVA squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix: preliminary report of a radiation therapy oncology group randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1987;13:541–549. - PubMed
-
- Piver MS, Barlow JJ, Vongtama V, Blumenson L. Hydroxyurea: a radiation potentiator in carcinoma of the uterine cervix. A randomized double-blind study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983;147:803–808. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

