Interaction of vitamin D receptor with HLA DRB1 0301 in type 1 diabetes patients from North India
- PMID: 19956544
- PMCID: PMC2780726
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008023
Interaction of vitamin D receptor with HLA DRB1 0301 in type 1 diabetes patients from North India
Abstract
Background: Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a multifactorial autoimmune disorder where interaction and integration of immune response genes along with environmental factors play a role in autoimmune destruction of the insulin producing Pancreatic Beta cells.
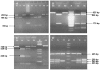
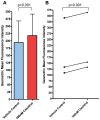
Methodology/principal findings: We have studied four single nucleotide polymorphisms (FokI site in Exon 2, BsmI and ApaI sites in Intron 8 and TaqI site in exon 9) in the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene using PCR-RFLP and HLA-DRB1 alleles using PCR and hybridization with sequence specific oligonucleotide probes and studied their interaction using LD based statistics for non-linked loci followed by sequence analysis of the vitamin D response element (VDRE) present in the promoter region of HLA-DRB1 0301. Haplotypes, constructed using SHEsis program for four single nucleotide polymorphisms in the VDR gene, were studied for their interaction with HLA-DRB1 alleles in 233 T1D patients and 191 healthy controls from North India. A significant increase of haplotypes FBAt and fBAT (p<0.02, OR = 1.44 and p<0.002, OR = 3.23 respectively) was observed in the patients. Both the haplotypes FBAt and fBAT were significantly increased in male patients with age at onset less than 18 years; however, fBAT was significantly increased in female patients irrespective of their age at onset. LD based statistics showed significant interaction between the high producer F and T alleles with HLA-DRB1 0301. F and T alleles of VDR have been shown to contribute to VDR mRNA independently. The promoter sequence analysis of HLA-DRB1 0301 showed presence of VDRE involved in higher expression of HLA-DRB1 030, which was confirmed by flow cytometry and real time PCR analysis.
Conclusions/significance: These data suggest that the interaction between VDR and HLA alleles is mediated by VDRE present in the promoter region of HLA-DRB1 0301 allele, which may be detrimental for the manifestation of T1D in the absence of 1,25-(OH)(2)D(3) in early childhood due to poor expression of DRB1 0301 in the thymus resulting in autoimmunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Krishnaswamy CV. Incidence of IDDM in children in urban population in southern India. Madras IDDM Registry Group Madras, South India. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1996;34:79–82. - PubMed
-
- Rani R, Sood A, Goswami R. Molecular basis of predisposition to develop type 1 diabetes mellitus in North Indians. Tissue Antigens. 2004;64:145–155. - PubMed
-
- Kumar R, Goswami R, Agarwal S, Israni N, Singh SK, et al. Association and interaction of the TNF-alpha gene with other pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine genes and HLA genes in patients with type 1 diabetes from North India. Tissue Antigens. 2007;69:557–567. - PubMed
-
- Boonstra A, Barrat FJ, Crain C, Heath VL, Savelkoul HF, et al. 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin d3 has a direct effect on naive CD4(+) T cells to enhance the development of Th2 cells. J Immunol. 2001;167:4974–4980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

