CD38/CD31 interactions activate genetic pathways leading to proliferation and migration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
- PMID: 19956559
- PMCID: PMC2785473
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2009.00146
CD38/CD31 interactions activate genetic pathways leading to proliferation and migration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
Abstract
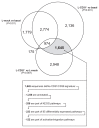
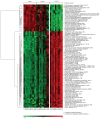
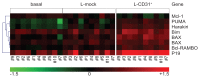
Human CD38 is a pleiotropic glycoprotein belonging to a family of enzymes/receptors involved in the catabolism of extracellular nucleotides. CD38-receptor activities are regulated through binding to the nonsubstrate ligand CD31. CD38 expression above a critical threshold is a negative prognostic marker for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients. Activation of CD38 by means of agonistic monoclonal antibodies or the CD31 ligand induces proliferation and immunoblast differentiation of CLL cells. Here we define the genetic signature that follows long-term in vitro interactions between CD38(+) CLL lymphocytes and CD31(+) cells. The emerging profile confirms that the CD31/CD38 axis activates genetic programs relevant for proliferative responses. It also indicates a contribution of this pathway to the processes mediating migration and homing. These results further support the notion that the CD31/CD38 axis is part of a network of accessory signals that modify the microenvironment, favoring localization of leukemic cells to growth-permissive sites.
Figures
Similar articles
-
No convincing evidence for a role of CD31-CD38 interactions in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Blood. 2008 Aug 1;112(3):840-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-144576. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18519815
-
In-tandem insight from basic science combined with clinical research: CD38 as both marker and key component of the pathogenetic network underlying chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Blood. 2006 Aug 15;108(4):1135-44. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-01-013003. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16621959 Review.
-
CD38 and CD100 lead a network of surface receptors relaying positive signals for B-CLL growth and survival.Blood. 2005 Apr 15;105(8):3042-50. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-3873. Epub 2004 Dec 21. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15613544
-
The enzymatic activities of CD38 enhance CLL growth and trafficking: implications for therapeutic targeting.Leukemia. 2015 Feb;29(2):356-68. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.207. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Leukemia. 2015. PMID: 24990614
-
Multiple metamorphoses of CD38 from prognostic marker to disease modifier to therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(23):2955-64. doi: 10.2174/15680266113136660210. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24171772 Review.
Cited by
-
HIV Disease Progression: Overexpression of the Ectoenzyme CD38 as a Contributory Factor?Bioessays. 2019 Jan;41(1):e1800128. doi: 10.1002/bies.201800128. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Bioessays. 2019. PMID: 30537007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PI3K p110δ regulates expression of CD38 on regulatory T cells.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 1;6(3):e17359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017359. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21390257 Free PMC article.
-
The pathogenic relevance of the prognostic markers CD38 and CD49d in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Ann Hematol. 2014 Mar;93(3):361-74. doi: 10.1007/s00277-013-1967-y. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Ann Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24288111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of CD38 expression in Sudanese patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.BMC Res Notes. 2018 Nov 15;11(1):815. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3926-0. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 30442182 Free PMC article.
-
Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Is Involved in the CD38 Signal Transduction Pathway in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 30;11(12):e0169159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169159. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 28036404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malavasi F, Deaglio S, Funaro A, et al. Evolution and function of the ADP ribosyl cyclase/CD38 gene family in physiology and pathology. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:841–886. - PubMed
-
- Deaglio S, Mallone R, Baj G, et al. CD38/CD31, a receptor/ligand system ruling adhesion and signaling in human leukocytes. Chem Immunol. 2000;75:99–120. - PubMed
-
- Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;94:1840–1847. - PubMed
-
- Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, et al. ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1764–1775. - PubMed
-
- Matrai Z. CD38 as a prognostic marker in CLL. Hematology. 2005;10:39–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

