A genome-wide survey for host response of silkworm, Bombyx mori during pathogen Bacillus bombyseptieus infection
- PMID: 19956592
- PMCID: PMC2780328
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008098
A genome-wide survey for host response of silkworm, Bombyx mori during pathogen Bacillus bombyseptieus infection
Abstract
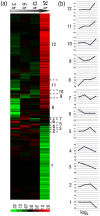
Host-pathogen interactions are complex relationships, and a central challenge is to reveal the interactions between pathogens and their hosts. Bacillus bombysepticus (Bb) which can produces spores and parasporal crystals was firstly separated from the corpses of the infected silkworms (Bombyx mori). Bb naturally infects the silkworm can cause an acute fuliginosa septicaemia and kill the silkworm larvae generally within one day in the hot and humid season. Bb pathogen of the silkworm can be used for investigating the host responses after the infection. Gene expression profiling during four time-points of silkworm whole larvae after Bb infection was performed to gain insight into the mechanism of Bb-associated host whole body effect. Genome-wide survey of the host genes demonstrated many genes and pathways modulated after the infection. GO analysis of the induced genes indicated that their functions could be divided into 14 categories. KEGG pathway analysis identified that six types of basal metabolic pathway were regulated, including genetic information processing and transcription, carbohydrate metabolism, amino acid and nitrogen metabolism, nucleotide metabolism, metabolism of cofactors and vitamins, and xenobiotic biodegradation and metabolism. Similar to Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), Bb can also induce a silkworm poisoning-related response. In this process, genes encoding midgut peritrophic membrane proteins, aminopeptidase N receptors and sodium/calcium exchange protein showed modulation. For the first time, we found that Bb induced a lot of genes involved in juvenile hormone synthesis and metabolism pathway upregulated. Bb also triggered the host immune responses, including cellular immune response and serine protease cascade melanization response. Real time PCR analysis showed that Bb can induce the silkworm systemic immune response, mainly by the Toll pathway. Anti-microorganism peptides (AMPs), including of Attacin, Lebocin, Enbocin, Gloverin and Moricin families, were upregulated at 24 hours post the infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





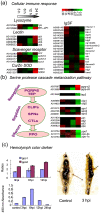
References
-
- Zegers ND, Kluter E, van Der Stap H, van Dura E, van Dalen P, et al. Expression of the protective antigen of Bacillus anthracis by Lactobacillus casei: towards the development of an oral vaccine against anthrax. J Appl Microbiol. 1999;87:309–314. - PubMed
-
- Jung JJ, Jeung HC, Lee JO, Kim TS, Chung HC, et al. Putative chemosensitivity predictive genes in colorectal cancer cell lines for anticancer agents. Oncol Rep. 2007;18:593–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

