Alleviation of high-fat diet-induced fatty liver damage in group IVA phospholipase A2-knockout mice
- PMID: 19956652
- PMCID: PMC2779103
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008089
Alleviation of high-fat diet-induced fatty liver damage in group IVA phospholipase A2-knockout mice
Abstract
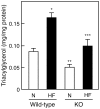
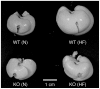
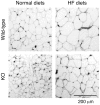
Hepatic fat deposition with hepatocellular damage, a feature of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, is mediated by several putative factors including prostaglandins. In the present study, we examined whether group IVA phospholipase A(2) (IVA-PLA(2)), which catalyzes the first step in prostanoid biosynthesis, is involved in the development of fatty liver, using IVA-PLA(2)-knockout mice. Male wild-type mice on high-fat diets (20% fat and 1.25% cholesterol) developed hepatocellular vacuolation and liver hypertrophy with an increase in the serum levels of liver damage marker aminotransferases when compared with wild-type mice fed normal diets. These high-fat diet-induced alterations were markedly decreased in IVA-PLA(2)-knockout mice. Hepatic triacylglycerol content was lower in IVA-PLA(2)-knockout mice than in wild-type mice under normal dietary conditions. Although high-fat diets increased hepatic triacylglycerol content in both genotypes, the degree was lower in IVA-PLA(2)-knockout mice than in wild-type mice. Under the high-fat dietary conditions, IVA-PLA(2)-knockout mice had lower epididymal fat pad weight and smaller adipocytes than wild-type mice. The serum level of prostaglandin E(2), which has a fat storage effect, was lower in IVA-PLA(2)-knockout mice than in wild-type mice, irrespective of the kind of diet. In both genotypes, high-fat diets increased serum leptin levels equally between the two groups, but did not affect the serum levels of adiponectin, resistin, free fatty acid, triacylglycerol, glucose, or insulin. Our findings suggest that a deficiency of IVA-PLA(2) alleviates fatty liver damage caused by high-fat diets, probably because of the lower generation of IVA-PLA(2) metabolites, such as prostaglandin E(2). IVA-PLA(2) could be a promising therapeutic target for obesity-related diseases including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Group IVA phospholipase A2 is associated with the storage of lipids in adipose tissue and liver.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2008 Jun;86(1-4):12-7. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2007.12.002. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2008. PMID: 18282778
-
Group IVA phospholipase A2-associated production of MMP-9 in macrophages and formation of atherosclerotic lesions.Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Mar;31(3):363-8. doi: 10.1248/bpb.31.363. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008. PMID: 18310893
-
Combined effects of rosiglitazone and conjugated linoleic acid on adiposity, insulin sensitivity, and hepatic steatosis in high-fat-fed mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):G1671-82. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00523.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17322064
-
Group IVA Phospholipase A2 in Collagen-Producing Cells Promotes High-Fat Diet-Induced Infiltration of Inflammatory Cells into the Liver by Upregulating the Expression of MCP-1.Biol Pharm Bull. 2024;47(5):1058-1065. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b24-00035. Biol Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 38825533
-
Mice deficient in group VIB phospholipase A2 (iPLA2gamma) exhibit relative resistance to obesity and metabolic abnormalities induced by a Western diet.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Jun;298(6):E1097-114. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00780.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20179248 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lipid zonation and phospholipid remodeling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatology. 2017 Apr;65(4):1165-1180. doi: 10.1002/hep.28953. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 27863448 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase activation ameliorates eicosanoid dysregulation in high-fat-induced kidney disease in mice.J Lipid Res. 2019 May;60(5):937-952. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M088690. Epub 2019 Mar 12. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30862696 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A₂: physiological function and role in disease.J Lipid Res. 2015 Aug;56(8):1386-402. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R057588. Epub 2015 Apr 2. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 25838312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rescue of Hepatic Phospholipid Remodeling Defectin iPLA2β-Null Mice Attenuates Obese but Not Non-Obese Fatty Liver.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 17;10(9):1332. doi: 10.3390/biom10091332. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32957701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of thiol antioxidant β-mercaptoethanol on diet-induced obese mice.Life Sci. 2014 Jun 27;107(1-2):32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.04.031. Epub 2014 May 5. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24802126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schaloske RH, Dennis EA. The phospholipase A2 superfamily and its group numbering system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1761:1246–1259. - PubMed
-
- Ii H, Hatakeyama S, Tsutsumi K, Sato T, Akiba S. Group IVA phospholipase A2 is associated with the storage of lipids in adipose tissue and liver. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2008;86:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Pérez S, Aspichueta P, Ochoa B, Chico Y. The 2-series prostaglandins suppress VLDL secretion in an inflammatory condition-dependent manner in primary rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;176:160–171. - PubMed
-
- Enomoto N, Ikejima K, Yamashina S, Enomoto A, Nishiura T, et al. Kupffer cell-derived prostaglandin E2 is involved in alcohol-induced fat accumulation in rat liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G100–G106. - PubMed
-
- Mazid MA, Chowdhury AA, Nagao K, Nishimura K, Jisaka M, et al. Endogenous 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 synthesized by adipocytes during maturation phase contributes to upregulation of fat storage. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:6885–6890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

