GD3 synthase overexpression sensitizes hepatocarcinoma cells to hypoxia and reduces tumor growth by suppressing the cSrc/NF-kappaB survival pathway
- PMID: 19956670
- PMCID: PMC2777380
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008059
GD3 synthase overexpression sensitizes hepatocarcinoma cells to hypoxia and reduces tumor growth by suppressing the cSrc/NF-kappaB survival pathway
Abstract
Background: Hypoxia-mediated HIF-1alpha stabilization and NF-kappaB activation play a key role in carcinogenesis by fostering cancer cell survival, angiogenesis and tumor invasion. Gangliosides are integral components of biological membranes with an increasingly recognized role as signaling intermediates. In particular, ganglioside GD3 has been characterized as a proapoptotic lipid effector by promoting cell death signaling and suppression of survival pathways. Thus, our aim was to analyze the role of GD3 in hypoxia susceptibility of hepatocarcinoma cells and in vivo tumor growth.
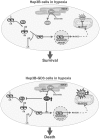
Methodology/principal findings: We generated and characterized a human hepatocarcinoma cell line stably expressing GD3 synthase (Hep3B-GD3), which catalyzes the synthesis of GD3 from GM3. Despite increased GD3 levels (2-3 fold), no significant changes in cell morphology or growth were observed in Hep3B-GD3 cells compared to wild type Hep3B cells under normoxia. However, exposure of Hep3B-GD3 cells to hypoxia (2% O(2)) enhanced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, resulting in decreased cell survival, with similar findings observed in Hep3B cells exposed to increasing doses of exogenous GD3. In addition, hypoxia-induced c-Src phosphorylation at tyrosine residues, NF-kappaB activation and subsequent expression of Mn-SOD were observed in Hep3B cells but not in Hep3B-GD3 cells. Moreover, MnTBAP, an antioxidant with predominant SOD mimetic activity, reduced ROS generation, protecting Hep3B-GD3 cells from hypoxia-induced death. Finally, lower tumor growth, higher cell death and reduced Mn-SOD expression were observed in Hep3B-GD3 compared to Hep3B tumor xenografts.
Conclusion: These findings underscore a role for GD3 in hypoxia susceptibility by disabling the c-Src/NF-kappaB survival pathway resulting in lower Mn-SOD expression, which may be of relevance in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
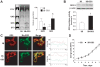
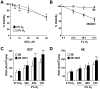
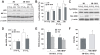
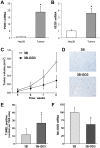
Similar articles
-
Dual role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in hypoxia signaling: activation of nuclear factor-{kappa}B via c-SRC and oxidant-dependent cell death.Cancer Res. 2007 Aug 1;67(15):7368-77. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0515. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17671207
-
Ganglioside GD3 sensitizes human hepatoma cells to cancer therapy.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 20;277(51):49870-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208303200. Epub 2002 Sep 25. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12351644
-
Anthocyanins Derived from Vitis coignetiae Pulliat Contributes Anti-Cancer Effects by Suppressing NF-κB Pathways in Hep3B Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells and In Vivo.Molecules. 2020 Nov 20;25(22):5445. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225445. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33233701 Free PMC article.
-
S100A8 and S100A9 are novel nuclear factor kappa B target genes during malignant progression of murine and human liver carcinogenesis.Hepatology. 2009 Oct;50(4):1251-62. doi: 10.1002/hep.23099. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19670424
-
A glycosphingolipid/caveolin-1 signaling complex inhibits motility of human ovarian carcinoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 25;286(47):40900-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.286146. Epub 2011 Sep 23. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21949119 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Current state-of-the-art on ganglioside-mediated immune modulation in the tumor microenvironment.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Sep;42(3):941-958. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10108-z. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37266839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the GD3 acetylation pathway selectively induces apoptosis in glioblastoma.Neuro Oncol. 2011 Sep;13(9):950-60. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor108. Epub 2011 Jul 31. Neuro Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21807667 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosphingolipids and cell death: one aim, many ways.Apoptosis. 2015 May;20(5):607-20. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1092-6. Apoptosis. 2015. PMID: 25637183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant polyphenols attenuate hepatic injury after hemorrhage/resuscitation by inhibition of apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation via NF-kappaB in rats.Eur J Nutr. 2012 Apr;51(3):311-21. doi: 10.1007/s00394-011-0216-1. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Eur J Nutr. 2012. PMID: 21698494
-
MiR-383 is downregulated in medulloblastoma and targets peroxiredoxin 3 (PRDX3).Brain Pathol. 2013 Jul;23(4):413-25. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12014. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Brain Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23227829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denko NC. Hypoxia, HIF1 and glucose metabolism in the solid tumor. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:705–713. - PubMed
-
- Guzy RD, Hoyos B, Robin E, Chen H, Liu L, et al. Mitochondrial complex III is required for hypoxia-induced ROS production and cellular oxygen sensing. Cell Metab. 2005;1:401–408. - PubMed
-
- Lluis JM, Buricchi F, Chiarugi P, Morales A, Fernandez-Checa JC. Dual role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in hypoxia signaling: activation of nuclear factor-(kappa}B via c-SRC and oxidant-dependent cell death. Cancer Res. 2007;67:7368–7377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

