Genevestigator v3: a reference expression database for the meta-analysis of transcriptomes
- PMID: 19956698
- PMCID: PMC2777001
- DOI: 10.1155/2008/420747
Genevestigator v3: a reference expression database for the meta-analysis of transcriptomes
Abstract
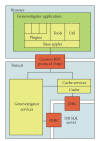
The Web-based software tool Genevestigator provides powerful tools for biologists to explore gene expression across a wide variety of biological contexts. Its first releases, however, were limited by the scaling ability of the system architecture, multiorganism data storage and analysis capability, and availability of computationally intensive analysis methods. Genevestigator V3 is a novel meta-analysis system resulting from new algorithmic and software development using a client/server architecture, large-scale manual curation and quality control of microarray data for several organisms, and curation of pathway data for mouse and Arabidopsis. In addition to improved querying features, Genevestigator V3 provides new tools to analyze the expression of genes in many different contexts, to identify biomarker genes, to cluster genes into expression modules, and to model expression responses in the context of metabolic and regulatory networks. Being a reference expression database with user-friendly tools, Genevestigator V3 facilitates discovery research and hypothesis validation.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

