Peloruside B, a potent antitumor macrolide from the New Zealand marine sponge Mycale hentscheli: isolation, structure, total synthesis, and bioactivity
- PMID: 19957922
- PMCID: PMC2812918
- DOI: 10.1021/jo9021265
Peloruside B, a potent antitumor macrolide from the New Zealand marine sponge Mycale hentscheli: isolation, structure, total synthesis, and bioactivity
Abstract
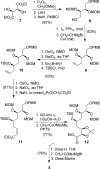
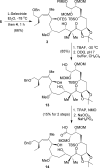
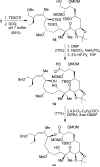
Peloruside B (2), a natural congener of peloruside A (1), was isolated in sub-milligram quantities from the New Zealand marine sponge Mycale hentscheli. Peloruside B promotes microtubule polymerization and arrests cells in the G(2)/M phase of mitosis similar to paclitaxel, and its bioactivity was comparable to that of peloruside A. NMR-directed isolation, structure elucidation, structure confirmation by total synthesis, and bioactivity of peloruside B are described in this article. The synthesis features Sharpless dihydroxylation, Brown's asymmetric allylboration reaction, reductive aldol coupling, Yamaguchi macrolactonization, and selective methylation.
Figures






References
-
- Perry NB, Blunt JW, Munro MHG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988;110:4851–4853.
-
- Perry NB, Blunt JW, Munro MHG, Thompson AM. J. Org. Chem. 1990;55:223–227.
-
- West LM, Northcote PT, Hood KA, Miller JH, Page MJ. J. Nat. Prod. 2000;63:707–709. - PubMed
-
- Northcote PT, Blunt JW, Munro MHG. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991;32:6411–6414.
-
- Burres NS, Clement JJ. Cancer Res. 1989;49:2935–2940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

