The implementation of e-learning tools to enhance undergraduate bioinformatics teaching and learning: a case study in the National University of Singapore
- PMID: 19958511
- PMCID: PMC2788352
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-S15-S12
The implementation of e-learning tools to enhance undergraduate bioinformatics teaching and learning: a case study in the National University of Singapore
Abstract
Background: The rapid advancement of computer and information technology in recent years has resulted in the rise of e-learning technologies to enhance and complement traditional classroom teaching in many fields, including bioinformatics. This paper records the experience of implementing e-learning technology to support problem-based learning (PBL) in the teaching of two undergraduate bioinformatics classes in the National University of Singapore.
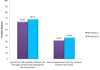
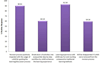
Results: Survey results further established the efficiency and suitability of e-learning tools to supplement PBL in bioinformatics education. 63.16% of year three bioinformatics students showed a positive response regarding the usefulness of the Learning Activity Management System (LAMS) e-learning tool in guiding the learning and discussion process involved in PBL and in enhancing the learning experience by breaking down PBL activities into a sequential workflow. On the other hand, 89.81% of year two bioinformatics students indicated that their revision process was positively impacted with the use of LAMS for guiding the learning process, while 60.19% agreed that the breakdown of activities into a sequential step-by-step workflow by LAMS enhances the learning experience
Conclusion: We show that e-learning tools are useful for supplementing PBL in bioinformatics education. The results suggest that it is feasible to develop and adopt e-learning tools to supplement a variety of instructional strategies in the future.
Figures
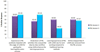
Similar articles
-
Towards a career in bioinformatics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Dec 3;10 Suppl 15(Suppl 15):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-S15-S1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19958508 Free PMC article.
-
BioManager: the use of a bioinformatics web application as a teaching tool in undergraduate bioinformatics training.Brief Bioinform. 2007 Nov;8(6):457-65. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbm039. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Brief Bioinform. 2007. PMID: 17715151 Review.
-
Development of an undergraduate bioinformatics degree program at a liberal arts college.Yale J Biol Med. 2012 Sep;85(3):309-21. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Yale J Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 23012579 Free PMC article.
-
Incubators: Building community networks and developing open educational resources to integrate bioinformatics into life science education.Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2020 Jul;48(4):381-390. doi: 10.1002/bmb.21387. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2020. PMID: 32585745 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating bioinformatics into senior high school: design principles and implications.Brief Bioinform. 2013 Sep;14(5):648-60. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbt030. Epub 2013 May 10. Brief Bioinform. 2013. PMID: 23665511 Review.
Cited by
-
Randomized Controlled Study of a Remote Flipped Classroom Neuro-otology Curriculum.Front Neurol. 2017 Jul 24;8:349. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00349. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28790966 Free PMC article.
-
A survey of scholarly literature describing the field of bioinformatics education and bioinformatics educational research.CBE Life Sci Educ. 2014 Winter;13(4):607-23. doi: 10.1187/cbe.13-10-0193. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2014. PMID: 25452484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics education--perspectives and challenges out of Africa.Brief Bioinform. 2015 Mar;16(2):355-64. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbu022. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Brief Bioinform. 2015. PMID: 24990350 Free PMC article.
-
Towards a career in bioinformatics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Dec 3;10 Suppl 15(Suppl 15):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-S15-S1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19958508 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Implementation of Hospital Automatic Nursing Management Information System Based on Computer Information Technology.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Dec 14;2021:1824300. doi: 10.1155/2021/1824300. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9845803. doi: 10.1155/2023/9845803. PMID: 34950222 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Friedman C, Altman R, Kohane I, McCormick K, Miller P, Ozbolt J. Training the next generation of informaticians: the impact of "BISTI" and bioinformatics--a report from the American College of Medical Informatics. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2004;11:167–172. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1520. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sahinidis NV, Harandi MT, Heath MT, Murphy L, Snir M, Wheeler RP, Zukoski CF. Establishing a master's degree programme in bioinformatics: challenges and opportunities. Syst Biol (Stevenage) 2005;152:269–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

