Recombinant porcine rotavirus VP4 and VP4-LTB expressed in Lactobacillus casei induced mucosal and systemic antibody responses in mice
- PMID: 19958557
- PMCID: PMC2797526
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-249
Recombinant porcine rotavirus VP4 and VP4-LTB expressed in Lactobacillus casei induced mucosal and systemic antibody responses in mice
Abstract
Background: Porcine rotavirus infection is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in the swine industry necessitating the development of effective vaccines for the prevention of infection. Immune responses associated with protection are primarily mucosal in nature and induction of mucosal immunity is important for preventing porcine rotavirus infection.
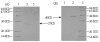
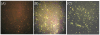
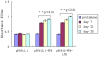
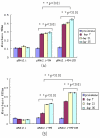
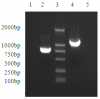
Results: Lactobacillus casei expressing the major protective antigen VP4 of porcine rotavirus (pPG612.1-VP4) or VP4-LTB (heat-labile toxin B subunit from Echerichia coli) (pPG612.1-VP4-LTB) fusion protein was used to immunize mice orally. The expression of recombinant pPG612.1-VP4 and pPG612.1-VP4-LTB was confirmed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis and surface-displayed expression on L. casei was verified by immunofluorescence. Mice orally immunized with recombinant protein-expressing L. casei produced high levels of serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) and mucosal IgA. The IgA titers from mice immunized with pPG612.1-VP4-LTB were higher than titters from pPG612.1-VP4-immunized mice. The induced antibodies demonstrated neutralizing effects on RV infection.
Conclusion: These results demonstrated that VP4 administered in the context of an L. casei expression system is an effective method for stimulating mucosal immunity and that LTB served to further stimulate mucosal immunity suggesting that this strategy can be adapted for use in pigs.
Figures
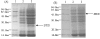
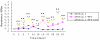

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the immune responses induced by oral immunization of mice with Lactobacillus casei-expressing porcine parvovirus VP2 and VP2 fused to Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit protein.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011 Jan;34(1):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2010.02.004. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 20226529 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Immunization with Lactobacillus casei Expressing the Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Cap and LTB Induces Mucosal and Systemic Antibody Responses in Mice.Viruses. 2021 Jul 5;13(7):1302. doi: 10.3390/v13071302. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34372508 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of recombinant Lactobacillus casei-expressing F4 (K88) fimbrial adhesin FaeG in conjunction with a heat-labile enterotoxin A (LTAK63) and heat-labile enterotoxin B (LTB) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli as an oral adjuvant in mice.J Appl Microbiol. 2017 Feb;122(2):506-515. doi: 10.1111/jam.13352. Epub 2016 Dec 12. J Appl Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27860074
-
Oral vaccination with the porcine rotavirus VP4 outer capsid protein expressed by Lactococcus lactis induces specific antibody production.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:708460. doi: 10.1155/2010/708460. Epub 2010 Jun 6. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20625406 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with recombinant Lactobacillus casei strains producing K99, K88 fimbrial protein protects mice against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Vaccine. 2012 May 9;30(22):3339-49. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.08.036. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Vaccine. 2012. PMID: 21856357
Cited by
-
Lactobacillus Mucosal Vaccine Vectors: Immune Responses against Bacterial and Viral Antigens.mSphere. 2018 May 16;3(3):e00061-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00061-18. eCollection 2018 May-Jun. mSphere. 2018. PMID: 29769376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined use of lactic-acid-producing bacteria as probiotics and rotavirus vaccine candidates expressing virus-specific proteins.Arch Virol. 2021 Apr;166(4):995-1006. doi: 10.1007/s00705-021-04964-9. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Arch Virol. 2021. PMID: 33533975 Review.
-
Rotavirus Infection in Swine: Genotypic Diversity, Immune Responses, and Role of Gut Microbiome in Rotavirus Immunity.Pathogens. 2022 Sep 22;11(10):1078. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11101078. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36297136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotic-Based Vaccines May Provide Effective Protection against COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Disease.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 May 6;9(5):466. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9050466. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flagellin in fusion with human rotavirus structural proteins exerts an adjuvant effect when delivered with replicating but non-disseminating adenovectors through the intrarectal route.Mol Biotechnol. 2014 May;56(5):394-407. doi: 10.1007/s12033-013-9723-z. Mol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24271565
References
-
- Estes MK. Rotaviruses and their replication. Fields Virology. 2001;4:1747–1785.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

