Radiation-related treatment effects across the age spectrum: differences and similarities or what the old and young can learn from each other
- PMID: 19959028
- PMCID: PMC2843498
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2009.09.001
Radiation-related treatment effects across the age spectrum: differences and similarities or what the old and young can learn from each other
Abstract
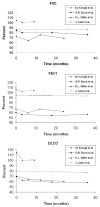
Radiation related effects in children and adults limit the delivery of effective radiation doses and result in long-term morbidity affecting function and quality of life. Improvements in our understanding of the etiology and biology of these effects, including the influence of clinical variables, dosimetric factors, and the underlying biological processes have made treatment safer and more efficacious. However, the approach to studying and understanding these effects differs between children and adults. Using the pulmonary and skeletal organ systems as examples, comparisons are made across the age spectrum for radiation related effects, including pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis, osteonecrosis, and fracture. Methods for dosimetric analysis, incorporation of imaging and biology as well a length of follow-up are compared, contrasted, and discussed for both organ systems in children and adults. Better understanding of each age specific approach and how it differs may improve our ability to study late effects of radiation across the ages.
Figures



References
-
- Moreno M, Aristu J, Ramos LI, et al. Predictive factors for radiation-induced pulmonary toxicity after three-dimensional conformal chemoradiation in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2007;9(9):596–602. - PubMed
-
- Kocak Z, Evans ES, Zhou SM, et al. Challenges in defining radiation pneumonitis in patients with lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;62(3):635–8. - PubMed
-
- Frankovich J, Donaldson SS, Lee Y, et al. High-dose therapy and autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation in children with primary refractory and relapsed Hodgkin’s disease: atopy predicts idiopathic diffuse lung injury syndromes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2001;7(1):49–57. - PubMed
-
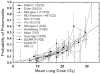
- Kwa SL, Lebesque JV, Theuws JC, et al. Radiation pneumonitis as a function of mean lung dose: an analysis of pooled data of 540 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;42(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Koh ES, Sun A, Tran TH, et al. Clinical dose-volume histogram analysis in predicting radiation pneumonitis in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66(1):223–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

