Role of RNA structure in regulating pre-mRNA splicing
- PMID: 19959365
- PMCID: PMC2834840
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.10.004
Role of RNA structure in regulating pre-mRNA splicing
Abstract
Pre-mRNA splicing involves removing non-coding introns from RNA transcripts. It is carried out by the spliceosome, along with other auxiliary factors. In general, research in splicing has focused on the sequences within the pre-mRNA, without considering the structures that these sequences might form. We propose that the role of RNA structure deserves more consideration when thinking about splicing mechanisms. RNA structures can inhibit or aid binding of spliceosomal components to the pre-mRNA, or can increase splicing efficiency by bringing important sequences into close proximity. Recent reports have identified proteins and small molecules that can regulate splicing by modulating RNA structures, thereby expanding our knowledge of the mechanisms used to regulate splicing.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

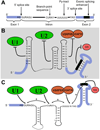
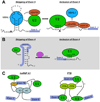

References
-
- Pan Q, et al. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat Genet. 2008;40(12):1413–1415. - PubMed
-
- Wahl MC, Will CL, Luhrmann R. The spliceosome: design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell. 2009;136(4):701–718. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, et al. RNA secondary structure and compensatory evolution. Genes Genet Syst. 1999;74(6):271–286. - PubMed
-
- Bentley DL. Rules of engagement: co-transcriptional recruitment of pre-mRNA processing factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17(3):251–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

