Whole-genome linkage and association scan in primary, nonsyndromic vesicoureteric reflux
- PMID: 19959718
- PMCID: PMC2799286
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2009060624
Whole-genome linkage and association scan in primary, nonsyndromic vesicoureteric reflux
Abstract
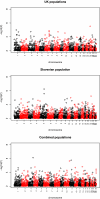
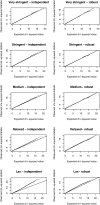
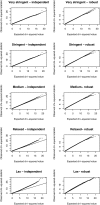
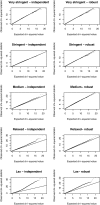
Primary vesicoureteric reflux accounts for approximately 10% of kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplantation, and sibling studies suggest a large genetic component. Here, we report a whole-genome linkage and association scan in primary, nonsyndromic vesicoureteric reflux and reflux nephropathy. We used linkage and family-based association approaches to analyze 320 white families (661 affected individuals, generally from families with two affected siblings) from two populations (United Kingdom and Slovenian). We found modest evidence of linkage but no clear overlap with previous studies. We tested for but did not detect association with six candidate genes (AGTR2, HNF1B, PAX2, RET, ROBO2, and UPK3A). Family-based analysis detected associations with one single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the UK families, with three SNPs in the Slovenian families, and with three SNPs in the combined families. A case-control analysis detected associations with three additional SNPs. The results of this study, which is the largest to date investigating the genetics of reflux, suggest that major loci may not exist for this common renal tract malformation within European populations.
Figures
References
-
- Risdon RA, Yeung CK, Ransley PG: Reflux nephropathy in children submitted to unilateral nephrectomy: A clinicopathological study. Clin Nephrol 40: 308–314, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Yeung CK, Godley ML, Dhillon HK, Gordon I, Duffy PG, Ransley PG: The characteristics of primary vesico-ureteric reflux in male and female infants with pre-natal hydronephrosis. Br J Urol 80: 319–327, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Williams G, Fletcher JT, Alexander SI, Craig JC: Vesicoureteral reflux. J Am Soc Nephrol 19: 847–862, 2008 - PubMed
-
- The Renal Association, UK Renal Registry, The Ninth Annual Report. Available at: http://www.renalreg.com/Reports/2006.html Accessed November 2, 2009
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

