Tumor suppressor scribble regulates assembly of tight junctions in the intestinal epithelium
- PMID: 19959811
- PMCID: PMC2797876
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090220
Tumor suppressor scribble regulates assembly of tight junctions in the intestinal epithelium
Abstract
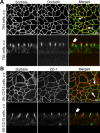
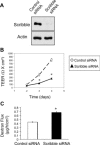
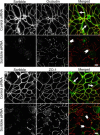
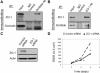
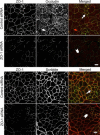
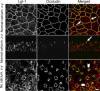
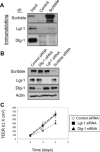
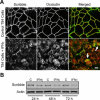
Formation of the epithelial barrier and apico-basal cell polarity represent two characteristics and mutually dependent features of differentiated epithelial monolayers. They are controlled by special adhesive structures, tight junctions (TJs), and polarity protein complexes that define the apical and the basolateral plasma membrane. The functional interplay between TJs and polarity complexes remains poorly understood. We investigated the role of Scribble, a basolateral polarity protein and known tumor suppressor, in regulating TJs in human intestinal epithelium. Scribble was enriched at TJs in T84 and SK-CO15 intestinal epithelial cell monolayers and sections of normal human colonic mucosa. siRNA-mediated knockdown of Scribble in SK-CO15 cells attenuated development of epithelial barrier and inhibited TJ reassembly independently of other basolateral polarity proteins Lgl-1 and Dlg-1. Scribble selectively co-imunoprecipitated with TJ protein ZO-1, and ZO-1 was important for Scribble recruitment to intercellular junctions and TJ reassembly. Lastly, Scribble was mislocalized from TJs and its expression down-regulated in interferon-gamma-treated T84 cell monolayers and inflamed human intestinal mucosa in vivo. We conclude that Scribble is an important regulator of TJ functions and plasticity in the intestinal epithelium. Down-regulation of Scribble may mediate mucosal barrier breakdown during intestinal inflammation.
Figures
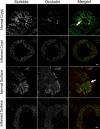
References
-
- Madara JL. Regulation of the movement of solutes across tight junctions. Annu Rev Physiol. 1998;60:143–159. - PubMed
-
- Basu TK, Donaldson D. Intestinal absorption in health and disease: micronutrients. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;17:957–979. - PubMed
-
- Lennernas H. Intestinal permeability and its relevance for absorption and elimination. Xenobiotica. 2007;37:1015–1051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R24DK 064399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R29 DK055679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM054712/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK 55679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 72564/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK064399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008169-21/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK061379/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK059888/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 61379/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072564/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

