The mechanisms underlying the generation of the colonic migrating motor complex in both wild-type and nNOS knockout mice
- PMID: 19959818
- PMCID: PMC2822500
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00399.2009
The mechanisms underlying the generation of the colonic migrating motor complex in both wild-type and nNOS knockout mice
Abstract
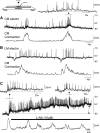
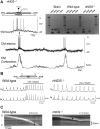
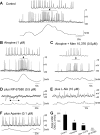
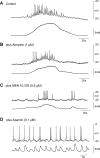
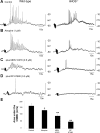
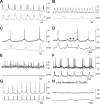
Colonic migrating motor complexes (CMMCs) propel fecal contents and are altered in diseased states, including slow-transit constipation. However, the mechanisms underlying the CMMCs are controversial because it has been proposed that disinhibition (turning off of inhibitory neurotransmission) or excitatory nerve activity generate the CMMC. Therefore, our aims were to reexamine the mechanisms underlying the CMMC in the colon of wild-type and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS)(-/-) mice. CMMCs were recorded from the isolated murine large bowel using intracellular recordings of electrical activity from circular muscle (CM) combined with tension recording. Spontaneous CMMCs occurred in both wild-type (frequency: 0.3 cycles/min) and nNOS(-/-) mice (frequency: 0.4 cycles/min). CMMCs consisted of a hyperpolarization, followed by fast oscillations (slow waves) with action potentials superimposed on a slow depolarization (wild-type: 14.0 +/- 0.6 mV; nNOS(-/-): 11.2 +/- 1.5 mV). Both atropine (1 microM) and MEN 10,376 [neurokinin 2 (NK2) antagonist; 0.5 microM] added successively reduced the slow depolarization and the number of action potentials but did not abolish the fast oscillations. The further addition of RP 67580 (NK1 antagonist; 0.5 microM) blocked the fast oscillations and the CMMC. Importantly, none of the antagonists affected the resting membrane potential, suggesting that ongoing tonic inhibition of the CM was maintained. Fecal pellet propulsion, which was blocked by the NK2 or the NK1 antagonist, was slower down the longer, more constricted nNOS(-/-) mouse colon (wild-type: 47.9 +/- 2.4 mm; nNOS(-/-): 57.8 +/- 1.4 mm). These observations suggest that excitatory neurotransmission enhances pacemaker activity during the CMMC. Therefore, the CMMC is likely generated by a synergistic interaction between neural and interstitial cells of Cajal networks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Critical role of 5-HT1A, 5-HT3, and 5-HT7 receptor subtypes in the initiation, generation, and propagation of the murine colonic migrating motor complex.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):G144-57. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00496.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20413719 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+ imaging of activity in ICC-MY during local mucosal reflexes and the colonic migrating motor complex in the murine large intestine.J Physiol. 2010 Nov 15;588(Pt 22):4453-74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.196824. Epub 2010 Sep 27. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20876203 Free PMC article.
-
Localized release of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) by a fecal pellet regulates migrating motor complexes in murine colon.Gastroenterology. 2009 Apr;136(4):1328-38. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.12.010. Epub 2008 Dec 10. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19138686 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium activity in different classes of myenteric neurons underlying the migrating motor complex in the murine colon.J Physiol. 2010 Feb 1;588(Pt 3):399-421. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.181172. Epub 2009 Nov 30. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19948652 Free PMC article.
-
A model of the enteric neural circuitry underlying the generation of rhythmic motor patterns in the colon: the role of serotonin.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;312(1):G1-G14. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00337.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27789457 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Agonist-dependent development of delta opioid receptor tolerance in the colon.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Aug;76(15):3033-3050. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03077-6. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30904952 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin and colonic motility.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015 Jul;27(7):899-905. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12617. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015. PMID: 26095115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights from a novel model of slow-transit constipation generated by partial outlet obstruction in the murine large intestine.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Nov 1;303(9):G1004-16. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00238.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22961801 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic neuromuscular transmission mediated by interstitial cells of Cajal in the myenteric layer in mouse ileal longitudinal smooth muscles.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014 Apr;387(4):377-88. doi: 10.1007/s00210-013-0944-2. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24322587
-
SCF-KIT signaling induces endothelin-3 synthesis and secretion: Thereby activates and regulates endothelin-B-receptor for generating temporally- and spatially-precise nitric oxide to modulate SCF- and or KIT-expressing cell functions.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 7;12(9):e0184154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184154. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28880927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albertí E, Mikkelsen HB, Wang XY, Díaz M, Larsen JO, Huizinga JD, Jiménez M. Pacemaker activity and inhibitory neurotransmission in the colon of Ws/Ws mutant rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292: G1499–G1510, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bayguinov PO, Hennig GW, Smith TK. Calcium imaging of myenteric neurons and ICC during local mucosal reflexes and the colonic migrating motor complex in the murine colon (Abstract). Neurogastroenterol Motil 21: 319, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Christensen J, Anuras S, Arthur C. Influence of intrinsic nerves on electromyogram of cat colon in vitro. Am J Physiol 234: E641–E647, 1978 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

