Human hematopoietic stem cells can survive in vitro for several months
- PMID: 19960048
- PMCID: PMC2778179
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/936761
Human hematopoietic stem cells can survive in vitro for several months
Abstract
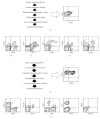
We previously reported that long-lasting in vitro hematopoiesis could be achieved using the cells differentiated from primate embryonic stem (ES) cells. Thus, we speculated that hematopoietic stem cells differentiated from ES cells could sustain long-lasting in vitro hematopoiesis. To test this hypothesis, we investigated whether human hematopoietic stem cells could similarly sustain long-lasting in vitro hematopoiesis in the same culture system. Although the results varied between experiments, presumably due to differences in the quality of each hematopoietic stem cell sample, long-lasting in vitro hematopoiesis was observed to last up to nine months. Furthermore, an in vivo analysis in which cultured cells were transplanted into immunodeficient mice indicated that even after several months of culture, hematopoietic stem cells were still present in the cultured cells. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to show that human hematopoietic stem cells can survive in vitro for several months.
Figures


References
-
- Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. The Lancet. 2008;371(9624):1579–1586. - PubMed
-
- Zon LI. Intrinsic and extrinsic control of haematopoietic stem-cell self-renewal. Nature. 2008;453(7193):306–313. - PubMed
-
- Heike T, Nakahata T. Ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells by cytokines. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2002;1592(3):313–321. - PubMed
-
- Ando K, Yahata T, Sato T, et al. Direct evidence for ex vivo expansion of human hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2006;107(8):3371–3377. - PubMed
-
- Dexter TM, Allen TD, Lajtha LG. Conditions controlling the proliferation of haemopoietic stem cells in vitro. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 1977;91(3):335–344. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

