Hypoxia-altered signaling pathways of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in human corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 19960069
- PMCID: PMC2787305
Hypoxia-altered signaling pathways of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in human corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
Purpose: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), a member of the TLR family, is an important pattern recognition molecule that plays a role in the host's innate immune responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a component of gram-negative bacteria. Contact lens wear is one of the risk factors for bacterial keratitis. The purpose of this study was to determine whether hypoxia or contact lens wear alters the TLR4 signaling pathways in human corneal epithelial cells (HCECs).
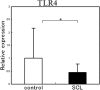
Method: A simian virus 40-immortalized human corneal epithelial cell (SV40-HCEC) line was cultured under 20% O2 or 2% O2 and exposed to LPS. The expression of TLR4, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and IL-8 was determined using a real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and immunoblotting. Immunoblotting was also used to determine whether the nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB) was activated in the SV40-HCEs. HCECs were obtained from 17 healthy volunteers and 18 hydrogel soft contact lens (SCL) wearers using impression cytology (IC), and the expression of the mRNA of TLR4 was determined using real-time RT-PCR.
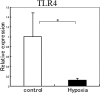
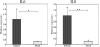
Results: A reduction in the expression of the mRNA and protein of TLR4 was detected in SV40-HCECs cultured under hypoxic conditions. Hypoxia also attenuated both the LPS-induced expression of IL-6 and IL-8, and the activation of NFkappaB in SV40-HCECs. The expression of the mRNA of TLR4 was down-regulated in the HCECs of soft contact lens wearers.
Conclusions: These results indicate that hypoxia attenuates the TLR4 signaling pathway in HCECs, suggesting that the increase in the susceptibility to bacterial infections under hypoxic conditions may be related to the TLR4 signaling pathways.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hypoxia attenuates inflammatory mediators production induced by Acanthamoeba via Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in human corneal epithelial cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Apr 13;420(3):685-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.069. Epub 2012 Mar 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22450324
-
Alteration of TLR3 pathways by glucocorticoids may be responsible for immunosusceptibility of human corneal epithelial cells to viral infections.Mol Vis. 2009 May 8;15:937-48. Mol Vis. 2009. PMID: 19452017 Free PMC article.
-
[Regulatory analysis of hypoxia on innate immunity of human corneal epithelium].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Nov 15;96(42):3408-3411. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.42.011. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27866535 Chinese.
-
Exogenous MD-2 confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness to human corneal epithelial cells with intracellular expression of TLR4 and CD14.Inflammation. 2011 Oct;34(5):371-8. doi: 10.1007/s10753-010-9244-x. Inflammation. 2011. PMID: 20700758
-
The Pathologic Role of Toll-Like Receptor 4 in Prostate Cancer.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 6;9:1188. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01188. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29928275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of differentially expressed genes in bacterial and fungal keratitis.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020 Jan;68(1):39-46. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_65_19. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31856463 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Hypoxia in Corneal Extracellular Matrix Deposition and Cell Motility.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020 Jun;303(6):1703-1716. doi: 10.1002/ar.24110. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 30861330 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus Hypoxia Adaptation Is Critical for the Establishment of Fungal Keratitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Apr 1;65(4):31. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.4.31. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38635243 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia preconditioning increases survival and decreases expression of Toll-like receptor 4 in pulmonary artery endothelial cells exposed to lipopolysaccharide.Pulm Circ. 2013 Sep;3(3):578-88. doi: 10.1086/674337. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Pulm Circ. 2013. PMID: 24618542 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic Stress Induced TREM-1 and Inflammatory Chemokines in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2014 Apr;29(2):133-8. doi: 10.1007/s12291-013-0345-9. Epub 2013 May 28. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24757292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Musch DC, Sugar A, Meyer RF. Demographic and predisposing factors in corneal ulceration. Arch Ophthalmol. 1983;101:1545–8. - PubMed
-
- Benson WH, Lanier JD. Current diagnosis and treatment of corneal ulcers. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1998;9:45–9. - PubMed
-
- Liesegang TJ. Contact lens-related microbial keratitis: Part I: Epidemiology. Cornea. 1997;16:125–31. - PubMed
-
- Cheng KH, Leung SL, Hoekman HW, Beekhuis WH, Mulder PG, Geerards AJ, Kijlstra A. Incidence of contact-lens-associated microbial keratitis and its related morbidity. Lancet. 1999;354:181–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
