Effects of heated humidification and topical steroids on compliance, nasal symptoms, and quality of life in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome using nasal continuous positive airway pressure
- PMID: 19961025
- PMCID: PMC2762712
Effects of heated humidification and topical steroids on compliance, nasal symptoms, and quality of life in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome using nasal continuous positive airway pressure
Abstract
Background: Nasal side effects are common in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) starting on nasal continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. We tested the hypothesis that heated humidification or nasal topical steroids improve compliance, nasal side effects and quality of life in this patient group.
Methods: 125 patients with the established diagnosis of OSAS (apnea/hypopnea index > or = 10/h), who tolerated CPAP via a nasal mask, and who had a successful CPAP titration were randomized to 4 weeks of dry CPAP, humidified CPAP or CPAP with additional topical nasal steroid application (fluticasone, GlaxoWellcome). Groups were similar in all demographic variables and in frequency of nasal symptoms at baseline. Outcome measures were objective compliance, quality of life (short form 36), subjective sleepiness (Epworth Sleepiness Scale score) and nasal symptoms such as runny, dry or blocked nose, sneezing and headaches; all variables assessed using a validated questionnaire and by direct interview.
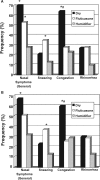
Results: There was no difference in compliance between groups after 4 weeks (dry: 5.21 +/- 1.66 h/night, fluticasone: 5.66 +/- 1.68, humidifier: 5.21 +/- 1.84; p = 0.444). Quality of life and subjective sleepiness improved in all groups, but there were no differences in the extent of improvement. Nasal Symptoms were less frequently reported in the humidifier group (28%) than in the remaining groups (dry: 70%, fluticasone: 53%, p = 0.002). However, the addition of fluticasone resulted in increased frequency of sneezing.
Conclusion: The addition of a humidifier, but not nasal steroids decreases the frequency of nasal symptoms in unselected OSAS patients initiating CPAP therapy; however compliance and quality of life remain unaltered.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of heated humidification on compliance and quality of life in patients with sleep apnea using nasal continuous positive airway pressure.Chest. 2005 Oct;128(4):2151-8. doi: 10.1378/chest.128.4.2151. Chest. 2005. PMID: 16236868 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Heated Humidification on CPAP Therapy Adherence in Subjects With Obstructive Sleep Apnea With Nasopharyngeal Symptoms.Respir Care. 2016 Sep;61(9):1151-9. doi: 10.4187/respcare.04536. Epub 2016 May 24. Respir Care. 2016. PMID: 27220350 Clinical Trial.
-
Heated humidification did not improve compliance of positive airway pressure and subjective daytime sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 5;13(12):e0207994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207994. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30517168 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of intranasal steroids on continuous positive airway pressure compliance among patients with obstructive sleep apnea.Sleep Breath. 2021 Sep;25(3):1293-1299. doi: 10.1007/s11325-020-02236-5. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Sleep Breath. 2021. PMID: 33104981 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of CPAP and mandibular advancement device treatment in obstructive sleep apnea patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sleep Breath. 2018 Sep;22(3):555-568. doi: 10.1007/s11325-017-1590-6. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Sleep Breath. 2018. PMID: 29129030
Cited by
-
The quest to improve CPAP adherence--PAP potpourri is not the answer.J Clin Sleep Med. 2012 Feb 15;8(1):49-50. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.1660. J Clin Sleep Med. 2012. PMID: 22334809 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Nasal Symptoms in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea and Their Association with Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Usage.Life (Basel). 2022 Feb 17;12(2):305. doi: 10.3390/life12020305. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207592 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in CPAP adherence over twenty years of data collection: a flattened curve.J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Aug 19;45(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s40463-016-0156-0. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016. PMID: 27542595 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of humidified versus nonhumidified CPAP on inflammatory response and nasopharyngeal symptoms in healthy participants.Can J Respir Ther. 2020 Jul 23;56:21-24. doi: 10.29390/cjrt-2020-005. eCollection 2020. Can J Respir Ther. 2020. PMID: 32844111 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of nasal abnormalities in adherence to continuous positive airway pressure device therapy in obstructive sleep apnea patients.Sleep Breath. 2013 Dec;17(4):1201-7. doi: 10.1007/s11325-013-0824-5. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Sleep Breath. 2013. PMID: 23463254
References
-
- Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1217–39. - PubMed
-
- Nieto FJ, Young TB, Lind BK, et al. Association of sleep-disordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community-based study. Sleep Heart Health Study. JAMA. 2000;283:1829–36. - PubMed
-
- Shahar E, Whitney CW, Redline S, et al. Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease: cross-sectional results of the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:19–25. - PubMed
-
- Young T, Blustein J, Finn L, Palta M. Sleep-disordered breathing and motor vehicle accidents in a population-based sample of employed adults. Sleep. 1997;20:608–13. - PubMed
-
- Doherty LS, Kiely JL, Swan V, McNicholas WT. Long-term effects of nasal continuous positive airway pressure therapy on cardiovascular outcomes in sleep apnea syndrome. Chest. 2005;127:2076–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
