Loss of MTG16a (CBFA2T3), a novel rDNA repressor, leads to increased ribogenesis and disruption of breast acinar morphogenesis
- PMID: 19961547
- PMCID: PMC3828852
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00982.x
Loss of MTG16a (CBFA2T3), a novel rDNA repressor, leads to increased ribogenesis and disruption of breast acinar morphogenesis
Erratum in
- J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Aug;14(8):2186
Abstract
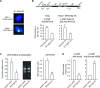
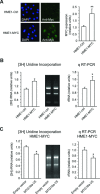
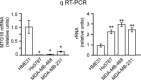
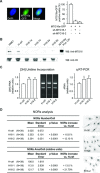
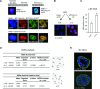
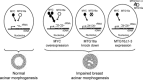
Human MTG16a (CBFA2T3), a chromatin repressor with nucleolar localization, was described to act as a suppressor of breast tumourigenesis. Here we show that MTG16a is a novel ribosomal gene repressor, which can counteract MYC-driven activation of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) transcription. We also show that either knocking down MTG16a by RNA interference, or sequestering MTG16a outside the nucleolus of human breast epithelial cells, hampers acinar morphogenesis concomitant with up-regulation of rRNA synthesis and increased ribogenesis. This is the first demonstration that loss of MTG16a function in the nucleolus of breast epithelial cells can induce morphological and molecular changes typical of breast cancer initiation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The transcriptional corepressor MTG16a contains a novel nucleolar targeting sequence deranged in t (16; 21)-positive myeloid malignancies.Oncogene. 2002 Sep 26;21(43):6703-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205882. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12242670
-
Che-1/AATF binds to RNA polymerase I machinery and sustains ribosomal RNA gene transcription.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 19;48(11):5891-5906. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa344. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32421830 Free PMC article.
-
DEAR1 is a dominant regulator of acinar morphogenesis and an independent predictor of local recurrence-free survival in early-onset breast cancer.PLoS Med. 2009 May 26;6(5):e1000068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000068. Epub 2009 May 5. PLoS Med. 2009. PMID: 19536326 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal RNA Transcription Regulation in Breast Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 29;12(4):502. doi: 10.3390/genes12040502. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifunctional nucleolus.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jul;8(7):574-85. doi: 10.1038/nrm2184. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17519961 Review.
Cited by
-
Undermining ribosomal RNA transcription in both the nucleolus and mitochondrion: an offbeat approach to target MYC-driven cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 22;9(4):5016-5031. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23579. eCollection 2018 Jan 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29435159 Free PMC article.
-
Mammary epithelial morphogenesis and early breast cancer. Evidence of involvement of basal components of the RNA Polymerase I transcription machinery.Cell Cycle. 2016 Sep 16;15(18):2515-26. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1215385. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27485818 Free PMC article.
-
3D Mammary Epithelial Cell Models: A Goldmine of DCIS Biomarkers and Morphogenetic Mechanisms.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jan 23;11(2):130. doi: 10.3390/cancers11020130. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30678048 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of RNA polymerase I transcription machinery in human malignancy: a clinical perspective.Onco Targets Ther. 2013 Jul 19;6:909-16. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S36627. Print 2013. Onco Targets Ther. 2013. PMID: 23888116 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing anti-cancer and cancer-promoting actions of all-trans retinoic acid in breast cancer to a RARα epigenetic mechanism of mammary epithelial cell fate.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 27;7(52):87064-87080. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13500. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27894085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boisvert FM, van Koningsbruggen S, Navascues J, et al. The multifunctional nucleolus. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:574–85. - PubMed
-
- Grummt I. Life on a planet of its own: regulation of RNA polymerase I transcription in the nucleolus. Genes Dev. 2003;17:1691–702. - PubMed
-
- Grummt I. Different epigenetic layers engage in complex crosstalk to define the epigenetic state of mammalian rRNA genes. Hum Mol Genet. 2007:R21–7. 16 Spec No 1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

