Bioavailability of ibuprofen following oral administration of standard ibuprofen, sodium ibuprofen or ibuprofen acid incorporating poloxamer in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 19961574
- PMCID: PMC2796637
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6904-9-19
Bioavailability of ibuprofen following oral administration of standard ibuprofen, sodium ibuprofen or ibuprofen acid incorporating poloxamer in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare the pharmacokinetic properties of sodium ibuprofen and ibuprofen acid incorporating poloxamer with standard ibuprofen acid tablets.
Methods: Twenty-two healthy volunteers were enrolled into this randomised, single-dose, 3-way crossover, open-label, single-centre, pharmacokinetic study. After 14 hours' fasting, participants received a single dose of 2x200 mg ibuprofen acid tablets (standard ibuprofen), 2x256 mg ibuprofen sodium dihydrate tablets (sodium ibuprofen; each equivalent to 200 mg ibuprofen acid) and 2x200 mg ibuprofen acid incorporating 60 mg poloxamer 407 (ibuprofen/poloxamer). A washout period of 2-7 days separated consecutive dosing days. On each of the 3 treatment days, blood samples were collected post dose for pharmacokinetic analyses and any adverse events recorded. Plasma concentration of ibuprofen was assessed using a liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometry procedure in negative ion mode. A standard statistical ANOVA model, appropriate for bioequivalence studies, was used and ratios of 90% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.
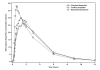
Results: Tmax for sodium ibuprofen was less than half that of standard ibuprofen (median 35 min vs 90 min, respectively; P=0.0002) and Cmax was significantly higher (41.47 microg/mL vs 31.88 microg/mL; ratio test/reference=130.06%, 90% CI 118.86-142.32%). Ibuprofen/poloxamer was bioequivalent to the standard ibuprofen formulation, despite its Tmax being on average 20 minutes shorter than standard ibuprofen (median 75 mins vs 90 mins, respectively; P=0.1913), as the ratio of test/reference=110.48% (CI 100.96-120.89%), which fell within the 80-125% limit of the CPMP and FDA guidelines for bioequivalence. The overall extent of absorption was similar for the three formulations, which were all well tolerated.
Conclusion: In terms of Tmax, ibuprofen formulated as a sodium salt was absorbed twice as quickly as from standard ibuprofen acid. The addition of poloxamer to ibuprofen acid did not significantly affect absorption.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Bioavailability Study of a New Orodispersible Formulation of Ibuprofen Versus Two Existing Oral Tablet Formulations in Healthy Male and Female Volunteers.Clin Ther. 2019 Aug;41(8):1486-1498. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.04.040. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Clin Ther. 2019. PMID: 31202508 Clinical Trial.
-
Rectal Administration of Ibuprofen: Comparison of Enema and Suppository Form.Drug Res (Stuttg). 2022 Jan;72(1):18-22. doi: 10.1055/a-1577-2955. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2022. PMID: 34416778 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative bioavailability of three ibuprofen formulations in healthy human volunteers.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Jun;46(6):309-18. doi: 10.5414/cpp46309. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18541128 Clinical Trial.
-
Ibuprofen lysinate, quicker and less variable: relative bioavailability compared to ibuprofen base in a pediatric suspension dosage form.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Nov;53(11):972-9. doi: 10.5414/CP202368. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26249766 Clinical Trial.
-
The pharmacokinetic profile of a novel fixed-dose combination tablet of ibuprofen and paracetamol.BMC Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Jul 5;10:10. doi: 10.1186/1472-6904-10-10. BMC Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20602760 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive evaluation of ibuprofenate amino acid isopropyl esters: insights into antioxidant activity, cytocompatibility, and cyclooxygenase inhibitory potential.Pharmacol Rep. 2024 Dec;76(6):1470-1481. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00666-6. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Pharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39425885 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the Type of Amino Acid on the Permeability and Properties of Ibuprofenates of Isopropyl Amino Acid Esters.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 9;23(8):4158. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084158. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456976 Free PMC article.
-
Fingerprinting of neurotoxic compounds using a mouse embryonic stem cell dual luminescence reporter assay.Arch Toxicol. 2017 Jan;91(1):365-391. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1690-2. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27015953 Free PMC article.
-
New amino acid propyl ester ibuprofenates from synthesis to use in drug delivery systems.RSC Adv. 2022 Dec 14;12(55):35779-35792. doi: 10.1039/d2ra05804a. eCollection 2022 Dec 12. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36545107 Free PMC article.
-
Onset of analgesia with sodium ibuprofen, ibuprofen acid incorporating poloxamer and acetaminophen--a single-dose, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with post-operative dental pain.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;65(4):343-53. doi: 10.1007/s00228-009-0614-y. Epub 2009 Feb 28. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19252905 Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources