Role of host genetics in fibrosis
- PMID: 19961576
- PMCID: PMC2796989
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-1536-2-6
Role of host genetics in fibrosis
Abstract
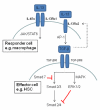
Fibrosis can occur in tissues in response to a variety of stimuli. Following tissue injury, cells undergo transformation or activation from a quiescent to an activated state resulting in tissue remodelling. The fibrogenic process creates a tissue environment that allows inflammatory and matrix-producing cells to invade and proliferate. While this process is important for normal wound healing, chronicity can lead to impaired tissue structure and function.This review examines the major factors involved in transforming or activating tissues towards fibrosis. The role of genetic variation within individuals affected by fibrosis has not been well described and it is in this context that we have examined the mediators of remodelling, including transforming growth factor-beta, T helper 2 cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases.Finally we examine the role of Toll-like receptors in fibrosis. The inflammatory phenotype that precedes fibrosis has been associated with Toll-like receptor activation. This is particularly important when considering gastrointestinal and hepatic disease, where inappropriate Toll-like receptor signalling, in response to the local microbe-rich environment, is thought to play an important role.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
The epidermal growth factor receptor ligand amphiregulin participates in the development of mouse liver fibrosis.Hepatology. 2008 Oct;48(4):1251-61. doi: 10.1002/hep.22437. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18634036
-
Hepatic fibrogenesis: the puzzle of interacting cells, fibrogenic cytokines, regulatory loops, and extracellular matrix molecules.Z Gastroenterol. 1992 Mar;30 Suppl 1:5-16. Z Gastroenterol. 1992. PMID: 1449018 Review.
-
The role of growth factors in peritoneal healing: transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta).Eur J Surg Suppl. 1997;(577):17-23. Eur J Surg Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9076448 Review.
-
Role of fibroblast growth factor signalling in hepatic fibrosis.Liver Int. 2021 Jun;41(6):1201-1215. doi: 10.1111/liv.14863. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Liver Int. 2021. PMID: 33655624 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α -G308A polymorphism is associated with liver pathological changes in hepatitis C virus patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep 14;22(34):7767-77. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7767. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27678360 Free PMC article.
-
Donor caveolin 1 (CAV1) genetic polymorphism influences graft function after renal transplantation.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2015 May 5;8:8. doi: 10.1186/s13069-015-0025-x. eCollection 2015. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2015. PMID: 25945124 Free PMC article.
-
Low-grade infections as a possible cause of arthrofibrosis after total knee arthroplasty.Patient Saf Surg. 2019 Jan 10;13:1. doi: 10.1186/s13037-018-0181-1. eCollection 2019. Patient Saf Surg. 2019. PMID: 30647774 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and treatment of hepatic fibrosis: is cirrhosis reversible?Clin Med (Lond). 2011 Apr;11(2):179-83. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.11-2-179. Clin Med (Lond). 2011. PMID: 21526707 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The Pressure of Aging.Med Clin North Am. 2017 Jan;101(1):81-101. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2016.08.006. Med Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 27884238 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

