Automated screening of monoclonal antibodies for SISCAPA assays using a magnetic bead processor and liquid chromatography-selected reaction monitoring-mass spectrometry
- PMID: 19961853
- PMCID: PMC2839902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2009.11.017
Automated screening of monoclonal antibodies for SISCAPA assays using a magnetic bead processor and liquid chromatography-selected reaction monitoring-mass spectrometry
Abstract
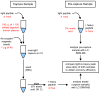
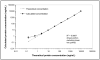
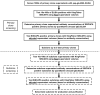
Stable Isotope Standards and Capture by Anti-Peptide Antibodies (SISCAPA) utilizes antibodies to enrich peptides from complex matrices for quantitation by stable isotope dilution mass spectrometry. SISCAPA improves sensitivity and limits the sample handling required for plasma-based analysis. Thus far, SISCAPA assays have been performed using polyclonal antibodies, yet monoclonal antibodies are an attractive alternative since they provide exquisite specificity, a renewable resource, and the potential for isolation of clones with very high affinities (10(-9) M or better). The selection of a good monoclonal antibody out of hundreds-to-thousands of clones presents a challenge, since the screening assay should ideally be in the format of the final SISCAPA assay, but performing the assays manually is labor- and time-intensive. In this manuscript, we demonstrate that monoclonal antibodies can be used in SISCAPA assays, and we describe an automated high-throughput SISCAPA method that makes screening of large numbers of hybridomas feasible while conserving time and resources.
2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SISCAPA peptide enrichment on magnetic beads using an in-line bead trap device.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 May;8(5):995-1005. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800446-MCP200. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19196707 Free PMC article.
-
An automated and multiplexed method for high throughput peptide immunoaffinity enrichment and multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry-based quantification of protein biomarkers.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 Jan;9(1):184-96. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900254-MCP200. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 19843560 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometric quantitation of peptides and proteins using Stable Isotope Standards and Capture by Anti-Peptide Antibodies (SISCAPA).J Proteome Res. 2004 Mar-Apr;3(2):235-44. doi: 10.1021/pr034086h. J Proteome Res. 2004. PMID: 15113099
-
Catch and measure-mass spectrometry-based immunoassays in biomarker research.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1844(5):927-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Sep 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24060810 Review.
-
Production and characterization of murine monoclonal antibody against synthetic peptide of CD34.Hum Antibodies. 2013;22(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.3233/HAB-130265. Hum Antibodies. 2013. PMID: 24284303 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequential multiplexed analyte quantification using peptide immunoaffinity enrichment coupled to mass spectrometry.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Jun;11(6):M111.015347. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.015347. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22203691 Free PMC article.
-
High-affinity recombinant antibody fragments (Fabs) can be applied in peptide enrichment immuno-MRM assays.J Proteome Res. 2014 Apr 4;13(4):2187-96. doi: 10.1021/pr4009404. Epub 2014 Mar 6. J Proteome Res. 2014. PMID: 24568200 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide and Protein Quantification Using Automated Immuno-MALDI (iMALDI).J Vis Exp. 2017 Aug 18;(126):55933. doi: 10.3791/55933. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28872133 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing the sensitivity of selected reaction monitoring-based targeted quantitative proteomics.Proteomics. 2012 Apr;12(8):1074-92. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100436. Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22577010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Multiplexed Assay for Oral Cancer Candidate Biomarkers Using Peptide Immunoaffinity Enrichment and Targeted Mass Spectrometry.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Oct;16(10):1829-1849. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA117.000147. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28821604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson NL, Anderson NG, Haines LR, Hardie DB, Olafson RW, Pearson TW. Mass spectrometric quantitation of peptides and proteins using Stable Isotope Standards and Capture by Anti-Peptide Antibodies (SISCAPA) J Proteome Res. 2004;3:235–244. - PubMed
-
- Berna M, Schmalz C, Duffin K, Mitchell P, Chambers M, Ackermann B. Online immunoaffinity liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry determination of a type II collagen peptide biomarker in rat urine: Investigation of the impact of collision-induced dissociation fluctuation on peptide quantitation. Anal Biochem. 2006;356:235–243. - PubMed
-
- Jiang J, Parker CE, Hoadley KA, Perou CM, Boysen G, Borchers CH. Development of an immuno tandem mass spectrometry (iMALDI) assay for EGFR diagnosis. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2007;1:1651–1659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

