Cyclic GMP/PKG-dependent inhibition of TRPC6 channel activity and expression negatively regulates cardiomyocyte NFAT activation Novel mechanism of cardiac stress modulation by PDE5 inhibition
- PMID: 19961855
- PMCID: PMC2837762
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.11.015
Cyclic GMP/PKG-dependent inhibition of TRPC6 channel activity and expression negatively regulates cardiomyocyte NFAT activation Novel mechanism of cardiac stress modulation by PDE5 inhibition
Abstract
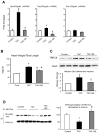
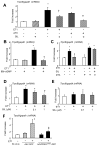
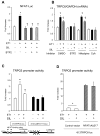
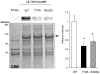
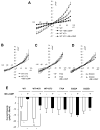
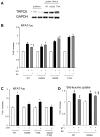
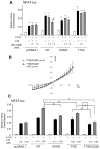
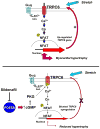
Increased cyclic GMP from enhanced synthesis or suppressed catabolism (e.g. PDE5 inhibition by sildenafil, SIL) activates protein kinase G (PKG) and blunts cardiac pathological hypertrophy. Suppressed calcineurin (Cn)-NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T-cells) signaling appears to be involved, though it remains unclear how this is achieved. One potential mechanism involves activation of Cn/NFAT by calcium entering via transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) channels (notably TRPC6). Here, we tested the hypothesis that PKG blocks Cn/NFAT activation by modifying and thus inhibiting TRPC6 current to break the positive feedback loop involving NFAT and NFAT-dependent TRPC6 upregulation. TRPC6 expression rose with pressure-overload in vivo, and angiotensin (ATII) or endothelin (ET1) stimulation in neonatal and adult cardiomyocytes in vitro. 8Br-cGMP and SIL reduced ET1-stimulated TRPC6 expression and NFAT dephosphorylation (activity). TRPC6 upregulation was absent if its promoter was mutated with non-functional NFAT binding sites, whereas constitutively active NFAT triggered TRPC6 expression that was not inhibited by SIL. PKG phosphorylated TRPC6, and both T70 and S322 were targeted. Both sites were functionally relevant, as 8Br-cGMP strongly suppressed current in wild-type TRPC6 channels, but not in those with phospho-silencing mutations (T70A, S322A or S322Q). NFAT activation and increased protein synthesis stimulated by ATII or ET1 was blocked by 8Br-cGMP or SIL. However, transfection with T70A or S322Q TRPC6 mutants blocked this inhibitory effect, whereas phospho-mimetic mutants (T70E, S322E, and both combined) suppressed NFAT activation. Thus PDE5-inhibition blocks TRPC6 channel activation and associated Cn/NFAT activation signaling by PKG-dependent channel phosphorylation.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

