Methusaleh's Zoo: how nature provides us with clues for extending human health span
- PMID: 19962715
- PMCID: PMC3535457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2009.10.024
Methusaleh's Zoo: how nature provides us with clues for extending human health span
Abstract
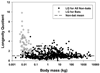
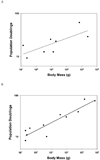
As impressive as the accomplishments of modern molecular biologists have been in finding genetic alterations that lengthen life in short-lived model organisms, they pale in comparison to the remarkable diversity of lifespans produced by evolution. Some animal species are now firmly documented to live for more than four centuries and even some mammals, like the bowhead whale, appear to survive 200 years or more. Another group of species may not be as absolutely long-lived, but they are remarkably long-lived for their body size and metabolic rate. These species include a number of bats, some of which live for at least 40 years in the wild, as well as the naked mole-rat, which is the same size, but lives nearly 10 times as long as the laboratory mouse. Together these exceptionally long-lived organisms have important roles to play in our future understanding of the causal mechanisms and modulation of ageing. Bats and naked mole-rats in particular have already contributed in the following ways: (1) they have contributed to the abandonment of the rate-of-living theory and weakened enthusiasm for the oxidative stress hypothesis of ageing, (2) they have helped evaluate how the tumour-suppressing role of cellular senescence is affected by the evolution of diverse body sizes as well as diverse longevities, (3) they have shed light on the relationship between specific types of DNA repair and ageing and (4) they have yielded insight into new processes, specifically the maintenance of the proteome and hypotheses concerning how evolution shapes ageing. The continuing acceleration of progress in genome sequencing and development of more and more cross-species investigatory techniques will facilitate even more contributions of these species in the near future.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author was an invited speaker at the Merial European Comparative Vaccinology Symposium and received travel expenses and an honorarium for this presentation.
Figures

References
-
- Allard M, Lebre V, Robine J-M. Jeanne Calment: from Van Gogh's Time to Ours. New York: WH Freeman & Co.; 1998.
-
- Andziak B, Buffenstein R. Disparate patterns of age-related changes in lipid peroxidation in long-lived naked mole-rats and shorter-lived mice. Aging Cell. 2006;5:525–532. - PubMed
-
- Andziak B, O'Connor TP, Qi W, DeWaal EM, Pierce A, et al. High oxidative damage levels in the longest-living rodent, the naked mole-rat. Aging Cell. 2006;5:463–471. - PubMed
-
- Anthony ELP, Kunz TH. Feeding strategies of the little brown bat, Myotis lucifugus, in southern New Hampshire. Ecology. 1977;58:775–786.
-
- Austad SN, Fischer KE. Mammalian aging, metabolism, and ecology: evidence from the bats and marsupials. Journal of Gerontology. 1991;46:B47–B53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

