Hypertension awareness, treatment, and control in adults with CKD: results from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study
- PMID: 19962808
- PMCID: PMC2866514
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.09.014
Hypertension awareness, treatment, and control in adults with CKD: results from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study
Abstract
Background: A low rate of blood pressure control has been reported in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). These data were derived from population-based samples with a low rate of CKD awareness.
Study design: Cross-sectional.
Setting & participants: Data from the baseline visit of the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study (n = 3,612) were analyzed. Participants with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 20-70 mL/min/1.73 m(2) were identified from physician offices and review of laboratory databases.
Outcomes: Prevalence and awareness of hypertension, treatment patterns, control rates, and factors associated with hypertension control.
Measurements: Following a standardized protocol, blood pressure was measured 3 times by trained staff, and hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure > or =140 mm Hg and/or diastolic blood pressure > or =90 mm Hg and/or self-reported antihypertensive medication use. Patients' awareness and treatment of hypertension were defined using self-report, and 2 levels of hypertension control were evaluated: systolic/diastolic blood pressure <140/90 and <130/80 mm Hg.
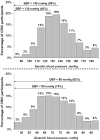
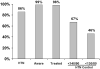
Results: The prevalence of hypertension was 85.7%, and 98.9% of CRIC participants were aware of this diagnosis and 98.3% were treated with medications, whereas 67.1% and 46.1% had hypertension controlled to <140/90 and <130/80 mm Hg, respectively. Of CRIC participants with hypertension, 15%, 25%, 26%, and 32% were using 1, 2, 3, and > or =4 antihypertensive medications, respectively. After multivariable adjustment, older patients, blacks, and those with higher urinary albumin excretion were less likely, whereas participants using angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers were more likely to have controlled their hypertension to <140/90 and <130/80 mm Hg.
Limitations: Data were derived from a single study visit.
Conclusions: Despite almost universal hypertension awareness and treatment in this cohort of patients with CKD, rates of hypertension control were suboptimal.
Copyright 2010 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
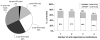
Comment in
-
Blood pressure control in CKD patients: why do we fail to implement the guidelines?Am J Kidney Dis. 2010 Mar;55(3):415-8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.12.013. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010. PMID: 20189048 No abstract available.
References
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:2038–2047. - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, Larson MG, Leip EP, Culleton B, Wilson PW, Levy D. Predictors of new-onset kidney disease in a community-based population. JAMA. 2004;291:844–850. - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Wei GL, McQuillan G, et al. Prevalence of high blood pressure and elevated serum creatinine level in the United States: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988-1994) Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:1207–1216. - PubMed
-
- Parikh NI, Hwang SJ, Larson MG, Meigs JB, Levy D, Fox CS. Cardiovascular disease risk factors in chronic kidney disease: overall burden and rates of treatment and control. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1884–1891. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK60980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK-06102/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK064860/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK060455/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007785/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

