Myosin isoform determines the conformational dynamics and cooperativity of actin filaments in the strongly bound actomyosin complex
- PMID: 19962990
- PMCID: PMC2834967
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.11.063
Myosin isoform determines the conformational dynamics and cooperativity of actin filaments in the strongly bound actomyosin complex
Abstract
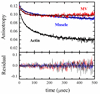
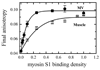
We used transient phosphorescence anisotropy to detect the microsecond rotational dynamics of erythrosin-iodoacetamide-labeled actin strongly bound to single-headed fragments of muscle myosin subfragment 1 (S1) and non-muscle myosin V (MV). The conformational dynamics of actin filaments in solution are markedly influenced by the isoform of bound myosin. Both myosins increase the final anisotropy of actin at substoichiometric binding densities, indicating long-range, non-nearest neighbor cooperative restriction of filament rotational dynamics amplitude, but the cooperative unit is larger with MV than with muscle S1. Both myosin isoforms also cooperatively affect the actin filament rotational correlation time, but with opposite effects: muscle S1 decreases rates of intrafilament torsional motion, while binding of MV increases the rates of motion. The cooperative effects on the rates of intrafilament motions correlate with the kinetics of myosin binding to actin filaments such that MV binds more rapidly and muscle myosin binds more slowly to partially decorated filaments than to bare filaments. The two isoforms also differ in their effects on the phosphorescence lifetime of the actin-bound erythrosin iodoacetamide: while muscle S1 increases the lifetime, suggesting decreased aqueous exposure of the probe, MV does not induce a significant change. We conclude that the dynamics and structure of actin in the strongly bound actomyosin complex are determined by the isoform of the bound myosin in a manner likely to accommodate the diverse functional roles of actomyosin in muscle and non-muscle cells.
Copyright (c) 2009. Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Actin filament dynamics in the actomyosin VI complex is regulated allosterically by calcium-calmodulin light chain.J Mol Biol. 2011 Oct 28;413(3):584-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.08.058. Epub 2011 Sep 6. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21910998 Free PMC article.
-
Differential dynamic behavior of actin filaments containing tightly-bound Ca2+ or Mg2+ in the presence of myosin heads actively hydrolyzing ATP.Biochemistry. 1999 Oct 5;38(40):13288-95. doi: 10.1021/bi990348a. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10529203
-
The structural dynamics of actin during active interaction with myosin depends on the isoform of the essential light chain.Biochemistry. 2013 Mar 5;52(9):1622-30. doi: 10.1021/bi3014467. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23339370 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in actin and myosin structural dynamics due to their weak and strong interactions.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002;36:7-19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-46558-4_2. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002. PMID: 11892285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-directed spectroscopic probes of actomyosin structural dynamics.Annu Rev Biophys. 2009;38:347-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.35.040405.102118. Annu Rev Biophys. 2009. PMID: 19416073 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myosin and tropomyosin stabilize the conformation of formin-nucleated actin filaments.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 14;287(38):31894-904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.341230. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22753415 Free PMC article.
-
G146V mutation at the hinge region of actin reveals a myosin class-specific requirement of actin conformations for motility.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 13;287(29):24339-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.321752. Epub 2012 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22637580 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution structures of the actomyosin-V complex in three nucleotide states provide insights into the force generation mechanism.Elife. 2021 Nov 23;10:e73724. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73724. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34812732 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-Scale Video Imaging of Motility Machinery by High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 10;15(2):257. doi: 10.3390/biom15020257. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The kinetics of cooperative cofilin binding reveals two states of the cofilin-actin filament.Biophys J. 2010 May 19;98(9):1893-901. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.01.023. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20441753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whittaker M, Wilson-Kubalek EM, Smith JE, Faust L, Milligan RA, Sweeney HL. A 35-A movement of smooth muscle myosin on ADP release. Nature. 1995;378:748–751. - PubMed
-
- Coureux PD, Wells AL, Menetrey J, Yengo CM, Morris CA, Sweeney HL, Houdusse A. A structural state of the myosin V motor without bound nucleotide. Nature. 2003;425:419–423. - PubMed
-
- Houdusse A, Sweeney HL. Myosin motors: missing structures and hidden springs. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001;11:182–194. - PubMed
-
- Volkmann N, Liu H, Hazelwood L, Krementsova EB, Lowey S, Trybus KM, Hanein D. The structural basis of myosin V processive movement as revealed by electron cryomicroscopy. Mol Cell. 2005;19:595–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

