Pharmacological activity of C10-substituted analogs of the high-affinity kainate receptor agonist dysiherbaine
- PMID: 19962997
- PMCID: PMC2813386
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.11.013
Pharmacological activity of C10-substituted analogs of the high-affinity kainate receptor agonist dysiherbaine
Abstract
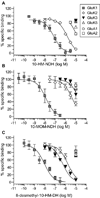
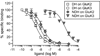
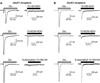
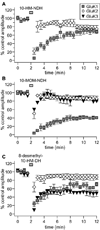
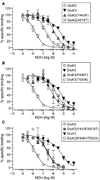
Kainate receptor antagonists have potential as therapeutic agents in a number of neuropathologies. Synthetic modification of the convulsant marine toxin neodysiherbaine A (NDH) previously yielded molecules with a diverse set of pharmacological actions on kainate receptors. Here we characterize three new synthetic analogs of NDH that contain substituents at the C10 position in the pyran ring of the marine toxin. The analogs exhibited high-affinity binding to the GluK1 (GluR5) subunit and lower affinity binding to GluK2 (GluR6) and GluK3 (GluR7) subunits in radioligand displacement assays with recombinant kainate and AMPA receptors. As well, the natural toxin NDH exhibited approximately 100-fold selectivity for GluK2 over GluK3 subunits, which was attributable to the C8 hydroxyl group in NDH. We used molecular dynamic simulations to determine the specific interactions between NDH and residues within the ligand-binding domains of these two kainate receptor subunits that contribute to the divergent apparent affinities for the compound. These data demonstrate that interactions with the GluK1 subunit are preserved in analogs with substitutions at C10 in NDH and further reveal the determinants of selectivity and pharmacological activity of molecules acting on kainate receptor subunits, which could aid in design of additional compounds that target these receptors.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

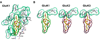
References
-
- Alt A, Weiss B, Ogden AM, Li X, Gleason SD, Calligaro DO, Bleakman D, Witkin JM. In vitro and in vivo studies in rats with LY293558 suggest AMPA/kainate receptor blockade as a novel potential mechanism for the therapeutic treatment of anxiety disorders. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2006;185:240–247. - PubMed
-
- Alt A, Weiss B, Ornstein PL, Gleason SD, Bleakman D, Stratford RE, Jr, Witkin JM. Anxiolytic-like effects through a GLU(K5) kainate receptor mechanism. Neuropharmacology. 2007;52:1482–1487. - PubMed
-
- Bayly C, Cieplak P, Cornell W, Kollman P. A well-behaved electrostatic potential based method using charge restraints for deriving atomic charges: the RESP model. J. Phys. Chem. 1993;97:10269–10280.
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Limbic seizure and brain damage produced by kainic acid: mechanisms and relevance to human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1985;14:375–403. - PubMed
-
- Cieplak P, Cornell W, Bayly C, Kollman P. Application of the multimolecule and multiconformational RESP methodology to biopolymers-charge derivation for DNA, RNA, and proteins. J. Comput. Chem. 1995;16:1357–1377.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

