Deblurring molecular images using desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- PMID: 19963935
- PMCID: PMC5003091
- DOI: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5332854
Deblurring molecular images using desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
Abstract
Traditional imaging techniques for studying the spatial distribution of biological molecules such as proteins, metabolites, and lipids, require the a priori selection of a handful of target molecules. Imaging mass spectrometry provides a means to analyze thousands of molecules at a time within a tissue sample, adding spatial detail to proteomic, metabolomic, and lipidomic studies. Compared to traditional microscopic images, mass spectrometric images have reduced spatial resolution and require a destructive acquisition process. In order to increase spatial detail, we propose a constrained acquisition path and signal degradation model enabling the use of a general image deblurring algorithm. Our analysis shows the potential of this approach and supports prior observations that the effect of the sprayer focuses on a central region much smaller than the extent of the spray.
Figures
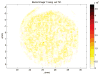



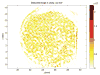
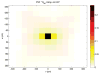
References
-
- McDonnell LA, Heeren RMA. Imaging mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrometry Reviews. 2007 Jul-Aug;26:606–643. - PubMed
-
- Pacholski ML, Winograd N. Imaging with mass spectrometry. Chemical Reviews. 1999 Oct;99:2977. - PubMed
-
- Kertesz V, Van Berkel GJ. Improved imaging resolution in desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry. 2008;22:2639–2644. - PubMed
-
- Takáts Z, Wiseman JM, Gologan B, Cooks RG. Mass spectrometry sampling under ambient conditions with desorption electrospray ionization. Science. 2004;306:471–473. - PubMed
-
- Roisman IV, Tropea C. Fluctuating flow in a liquid layer and secondary spray created by an impacting spray. International Journal of Multiphase Flow. 2005 Feb;31:179–200.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
