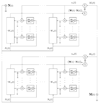
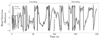
A biomimetic adaptive algorithm and low-power architecture for implantable neural decoders
- PMID: 19964345
- PMCID: PMC2905462
- DOI: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333793
A biomimetic adaptive algorithm and low-power architecture for implantable neural decoders
Abstract
Algorithmically and energetically efficient computational architectures that operate in real time are essential for clinically useful neural prosthetic devices. Such devices decode raw neural data to obtain direct control signals for external devices. They can also perform data compression and vastly reduce the bandwidth and consequently power expended in wireless transmission of raw data from implantable brain-machine interfaces. We describe a biomimetic algorithm and micropower analog circuit architecture for decoding neural cell ensemble signals. The decoding algorithm implements a continuous-time artificial neural network, using a bank of adaptive linear filters with kernels that emulate synaptic dynamics. The filters transform neural signal inputs into control-parameter outputs, and can be tuned automatically in an on-line learning process. We provide experimental validation of our system using neural data from thalamic head-direction cells in an awake behaving rat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficient universal computing architectures for decoding neural activity.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e42492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042492. Epub 2012 Sep 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984404 Free PMC article.
-
Circuit techniques for wireless brain interfaces.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009;2009:3213-6. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333160. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009. PMID: 19964058
-
Active microelectronic neurosensor arrays for implantable brain communication interfaces.IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2009 Aug;17(4):339-45. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2009.2024310. Epub 2009 Jun 5. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2009. PMID: 19502132 Free PMC article.
-
An implantable VLSI architecture for real time spike sorting in cortically controlled Brain Machine Interfaces.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:1569-72. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2010.5626691. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010. PMID: 21096383
-
Biomimetic brain machine interfaces for the control of movement.J Neurosci. 2007 Oct 31;27(44):11842-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3516-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17978021 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A glucose fuel cell for implantable brain-machine interfaces.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038436. Epub 2012 Jun 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22719888 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient universal computing architectures for decoding neural activity.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e42492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042492. Epub 2012 Sep 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984404 Free PMC article.
-
A chronic generalized bi-directional brain-machine interface.J Neural Eng. 2011 Jun;8(3):036018. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/8/3/036018. Epub 2011 May 5. J Neural Eng. 2011. PMID: 21543839 Free PMC article.
-
Physical principles for scalable neural recording.Front Comput Neurosci. 2013 Oct 21;7:137. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2013.00137. eCollection 2013. Front Comput Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24187539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chapin JK, Moxon KA, Markowitz RS, Nicolelis ML. Real-time control of a robot arm using simultaneously recorded neurons in the motor cortex. Nature Neuroscience. 1999;2:664–670. - PubMed
-
- Wessberg J, Stambaugh CR, Kralik JD, Beck PD, Laubach M, Chapin JK, Kim J, Biggs SJ, Srinivasan MA, Nicolelis MAL. Real-time prediction of hand trajectory by ensembles of cortical neurons in primates. Nature. 2000 November;408:361–365. - PubMed
-
- Taylor DM, Tillery SIH, Schwartz AB. Direct cortical control of 3d neuroprosthetic devices. Science. 2002 June;296:1829–1832. - PubMed
-
- Musallam S, Corneil BD, Greger B, Scherberger H, Andersen RA. Cognitive control signals for neural prosthetics. Science. 2004 July;305:258–262. - PubMed
-
- Hochberg LR, Serruya MD, Friehs GM, Mukand JA, Saleh M, Caplan AH, Branner A, Chen D, Penn RD, Donoghue JP. Neuronal ensemble control of prosthetic devices by a human with tetraplegia. Nature. 2006 July;442:164–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources