Lensless imaging for point-of-care testing
- PMID: 19964416
- PMCID: PMC3774534
- DOI: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333765
Lensless imaging for point-of-care testing
Abstract
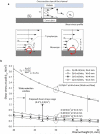
We show a platform that merges a microfluidic chip with lensless imaging for CD4(+) T-lymphocyte counting at resource-limited settings. To capture CD4(+) T lymphocytes, anti-CD4 antibody was immobilized on a microfluidic chip. The captured cells were detected by a charge coupled device (CCD) sensor using lensless shadow imaging techniques. Gray scale shadow images of captured cells on the chip (24 mm x 4 mm x 50 mum) were enumerated in three seconds using an automatic cell counting software. The device achieved 70.2 +/- 6.5% capture efficiency, 88.8 +/- 5.4% capture specificity for CD4(+) T-lymphocytes, 96 +/- 1.6% CCD efficiency, and 83.5 +/- 2.4% overall platform performance (n = 9 devices). This integrated platform has potential for point-of-care testing (POCT) to rapidly capture, image and count specific cell types from unprocessed whole blood.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrating microfluidics and lensless imaging for point-of-care testing.Biosens Bioelectron. 2009 Jul 15;24(11):3208-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2009.03.037. Epub 2009 Apr 2. Biosens Bioelectron. 2009. PMID: 19467854 Free PMC article.
-
On-chip sample preparation by controlled release of antibodies for simple CD4 counting.Lab Chip. 2012 Jan 7;12(1):167-73. doi: 10.1039/c1lc20565j. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Lab Chip. 2012. PMID: 22048158
-
Microfluidic CD4+ T-cell counting device using chemiluminescence-based detection.Anal Chem. 2010 Jan 1;82(1):36-40. doi: 10.1021/ac902144w. Anal Chem. 2010. PMID: 19938816
-
CD4 counting technologies for HIV therapy monitoring in resource-poor settings--state-of-the-art and emerging microtechnologies.Lab Chip. 2013 Jul 21;13(14):2731-48. doi: 10.1039/c3lc50213a. Lab Chip. 2013. PMID: 23670110 Review.
-
Lensless Imaging and Sensing.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2016 Jul 11;18:77-102. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-092515-010849. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2016. PMID: 27420569 Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring Neutropenia for Cancer Patients at the Point of Care.Small Methods. 2017 Sep 11;1(9):1700193. doi: 10.1002/smtd.201700193. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Small Methods. 2017. PMID: 30740513 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Image Sensors for Smart Analytical Chemiluminescence Biosensors.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Sep 12;11(9):912. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11090912. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39329654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hybrid Microscopy: Enabling Inexpensive High-Performance Imaging through Combined Physical and Optical Magnifications.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 15;6:22691. doi: 10.1038/srep22691. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26975883 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Bacterial and Viral Pathogens Using Photonic Point-of-Care Devices.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Oct 19;10(10):841. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10100841. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33086578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State of the Art in Smart Portable, Wearable, Ingestible and Implantable Devices for Health Status Monitoring and Disease Management.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 1;22(11):4228. doi: 10.3390/s22114228. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35684847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO . 2007 UNAIDS annual report: Knowing your epidemic. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS); GENEVA: 2008.
-
- Hammer SM, Eron JJ, Jr., Reiss P, Schooley RT, Thompson MA, Walmsley S, Cahn P, Fischl MA, Gatell JM, Hirsch MS, Jacobsen DM, Montaner JSG, Richman DD, Yeni PG, Volberding PA. Antiretroviral Treatment of Adult HIV Infection: 2008 Recommendations of the International AIDS Society-USA Panel. JAMA. 2008 Aug 6;300:555–570. 2008. - PubMed
-
- WHO . Patient Monitoring Guidelines for HIV Care and Antiretroviral Therapy. WHO; GENEVA: 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
