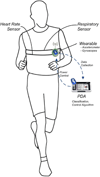
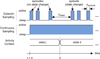
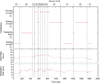
Episodic sampling: towards energy-efficient patient monitoring with wearable sensors
- PMID: 19964452
- PMCID: PMC5019958
- DOI: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333615
Episodic sampling: towards energy-efficient patient monitoring with wearable sensors
Abstract
Energy efficiency presents a critical design challenge in wireless, wearable sensor technology, mainly because of the associated diagnostic objectives required in each monitoring application. In order to maximize the operating lifetime during real-life monitoring and maintain sufficient classification accuracy, the wearable sensors require hardware support that allows dynamic power control on the sensors and wireless interfaces as well as monitoring algorithms to control these components intelligently. This paper introduces a context-aware sensing technique known as episodic sampling - a method of performing context classification only at specific time instances. Based on Additive-Increase/Multiplicative-Decrease (AIMD), episodic sampling demonstrates an energy reduction of 85 percent with a loss of only 5 percent in classification accuracy in our experiment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comprehensive survey of energy-aware routing protocols in wireless body area sensor networks.J Med Syst. 2016 Sep;40(9):201. doi: 10.1007/s10916-016-0556-8. Epub 2016 Jul 28. J Med Syst. 2016. PMID: 27468842
-
Wireless design of a multisensor system for physical activity monitoring.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2012 Nov;59(11):3230-7. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2208458. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2012. PMID: 23086196
-
Real-time daily activity classification with wireless sensor networks using Hidden Markov Model.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007;2007:3192-5. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4353008. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007. PMID: 18002674
-
Electroactive polymer-based devices for e-textiles in biomedicine.IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2005 Sep;9(3):295-318. doi: 10.1109/titb.2005.854514. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2005. PMID: 16167684 Review.
-
Smart fabrics and interactive textile enabling wearable personal applications: R&D state of the art and future challenges.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2008;2008:5270-3. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2008.4650403. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2008. PMID: 19163906 Review.
Cited by
-
A General Framework for Making Context-Recognition Systems More Energy Efficient.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jan 24;21(3):766. doi: 10.3390/s21030766. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33498804 Free PMC article.
-
Wearable Devices in Health Monitoring from the Environmental towards Multiple Domains: A Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;21(6):2130. doi: 10.3390/s21062130. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy-efficient context classification with dynamic sensor control.IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2012 Apr;6(2):167-78. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2011.2166073. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2012. PMID: 23852981 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adaptive Data Transmission Algorithm for the System of Inertial Sensors for Hand Movement Acquisition.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 15;22(24):9866. doi: 10.3390/s22249866. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560234 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of an acoustic gastrointestinal surveillance biosensor for postoperative ileus.J Gastrointest Surg. 2014 Oct;18(10):1795-803. doi: 10.1007/s11605-014-2597-y. Epub 2014 Aug 5. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014. PMID: 25091837
References
-
- Bonato P. Wearable Sensors/Systems and their Impact on Biomedical Engineering. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, IEEE. 2003 May-Jun;22(3):18–20. - PubMed
-
- Moy M, Mentzer S, Reilly J. Ambulatory Monitoring of Cumulative Free-Living Activity. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, IEEE. 2003 May-Jun;22(3):89–95. - PubMed
-
- Wu W, Batalin M, Au L, Bui A, Kaiser W. Context-aware Sensing of Physiological Signals; Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2007. EMBS 2007. 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE; 2007. Aug. pp. 5271–5275. - PubMed
-
- Gao T, Greenspan D, Welsh M, Juang R, Alm A. Vital Signs Monitoring and Patient Tracking Over a Wireless Network; Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2005. IEEE-EMBS 2005. 27th Annual International Conference of the; 2005. Jan. pp. 102–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources