Patch-basis electrocortical source imaging in epilepsy
- PMID: 19964603
- PMCID: PMC3039210
- DOI: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333992
Patch-basis electrocortical source imaging in epilepsy
Abstract
In this study, we developed numerical methods for investigating the sources of epileptic activity from intracranial EEG recordings acquired from intracranial subdural electrodes (iEEG) in patients undergoing pre-surgical evaluation at the epilepsy center of the Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN). The data were analyzed using independent component analysis (ICA), which identifies and isolates maximally independent signal components in multi-channel recordings. A realistic individual head model was constructed for a patient undergoing pre-surgical evaluation. Structural models of gray matter, white matter, CSF, skull, and scalp were extracted from pre-surgical MR and post-surgical CT images. The electromagnetic source localization forward problem was solved using the Boundary Element Method (BEM). Source localization was performed using the Sparse Bayesian Learning (SBL) algorithm. The multiscale patch-basis source space constructed for this purpose includes a large number of dipole elements on the cortical layer oriented perpendicular to the local cortical surface. These source dipoles are combined into overlapping multi-scalepatches. Using this approach, we were able to detect seizure activity on sulcal walls and on gyrus of the cortex.
Figures
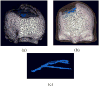

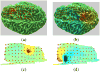

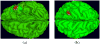
References
-
- Assaf BA, Ebersole JS. Continu ous Source Imaging of Scalp Ictal Rhythms in Temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1997;38(10):1114–1123. - PubMed
-
- Akalin Acar Z, Gencer NG. An advanced BEM implementation for the forward problem of Electro-magnetic source imaging. Physics in Med and Biol. 2004;49(5):5011–28. - PubMed
-
- Gencer NG, Akalin Acar Z. Use of the isolated problem approach for multi- compartment BEM models of electro-magnetic source imaging. Physics in Med and Biol. 2005;50:3007–22. - PubMed
-
- Ebersole JS, Hawes-Ebersole S. Clinical application of dipole models in the localization of epileptiform activity. J Clinical Neurophysiology. 2007;24(2):120–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
