Studies on expression and function of the TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel
- PMID: 19965375
- PMCID: PMC2781737
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911935106
Studies on expression and function of the TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel
Abstract
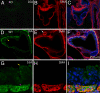
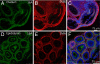
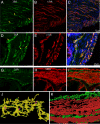
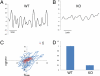
Calcium-activated chloride channels (CaCC) with similar hallmark features are present in many cell types and mediate important physiological functions including epithelial secretion, sensory signal transduction, and smooth muscle contraction. Having identified TMEM16A of the transmembrane proteins with unknown function (TMEM) 16 family as a CaCC subunit, we have developed antibodies specific for mouse TMEM16A, as evidenced by the absence of immunoreactivity in TMEM16A knockout mice. Here, we show that TMEM16A is located in the apical membranes of epithelial cells in exocrine glands and trachea. In addition, TMEM16A is expressed in airway smooth muscle cells and the smooth muscle cells of reproductive tracts, the oviduct and ductus epididymis. In the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, TMEM16A is absent from smooth muscle cells, but present in the interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC), the pacemaker cells that control smooth muscle contraction. The physiological importance of TMEM16A is underscored by the diminished rhythmic contraction of gastric smooth muscle from TMEM16A knockout mice. The TMEM16A expression pattern established in this study thus provides a roadmap for the analyses of physiological functions of calcium-activated chloride channels that contain TMEM16A subunits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Eggermont J. Calcium-activated chloride channels: (Un)known, (un)loved? Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2004;1:22–27. - PubMed
-
- Hartzell C, Putzier I, Arreola J. Calcium-activated chloride channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005;67:719–758. - PubMed
-
- Yang YD, et al. TMEM16A confers receptor-activated calcium-dependent chloride conductance. Nature. 2008;455:1210–1215. - PubMed
-
- Caputo A, et al. TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with calcium-dependent chloride channel activity. Science. 2008;322:590–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

