The Fanconi anemia pathway promotes replication-dependent DNA interstrand cross-link repair
- PMID: 19965384
- PMCID: PMC2909596
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1182372
The Fanconi anemia pathway promotes replication-dependent DNA interstrand cross-link repair
Abstract
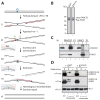
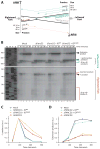
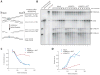
Fanconi anemia is a human cancer predisposition syndrome caused by mutations in 13 Fanc genes. The disorder is characterized by genomic instability and cellular hypersensitivity to chemicals that generate DNA interstrand cross-links (ICLs). A central event in the activation of the Fanconi anemia pathway is the mono-ubiquitylation of the FANCI-FANCD2 complex, but how this complex confers ICL resistance remains enigmatic. Using a cell-free system, we showed that FANCI-FANCD2 is required for replication-coupled ICL repair in S phase. Removal of FANCD2 from extracts inhibits both nucleolytic incisions near the ICL and translesion DNA synthesis past the lesion. Reversal of these defects requires ubiquitylated FANCI-FANCD2. Our results show that multiple steps of the essential S-phase ICL repair mechanism fail when the Fanconi anemia pathway is compromised.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

