Structural basis of immune evasion at the site of CD4 attachment on HIV-1 gp120
- PMID: 19965434
- PMCID: PMC2862588
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1175868
Structural basis of immune evasion at the site of CD4 attachment on HIV-1 gp120
Abstract
The site on HIV-1 gp120 that binds to the CD4 receptor is vulnerable to antibodies. However, most antibodies that interact with this site cannot neutralize HIV-1. To understand the basis of this resistance, we determined co-crystal structures for two poorly neutralizing, CD4-binding site (CD4BS) antibodies, F105 and b13, in complexes with gp120. Both antibodies exhibited approach angles to gp120 similar to those of CD4 and a rare, broadly neutralizing CD4BS antibody, b12. Slight differences in recognition, however, resulted in substantial differences in F105- and b13-bound conformations relative to b12-bound gp120. Modeling and binding experiments revealed these conformations to be poorly compatible with the viral spike. This incompatibility, the consequence of slight differences in CD4BS recognition, renders HIV-1 resistant to all but the most accurately targeted antibodies.
Figures
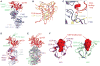
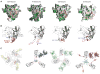
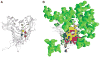
References
-
- UNAIDS. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2006. 2006 Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic. www.unaids.org/en/knowledgeCentre/HIVData/GlobalReport/2006/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

