Renal replacement therapy in infants with chronic renal failure in the first year of life
- PMID: 19965536
- PMCID: PMC2801652
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03670609
Renal replacement therapy in infants with chronic renal failure in the first year of life
Abstract
Background and objectives: Although results of renal replacement therapy (RRT) in small children have improved during recent years, data about RRT in neonates are scarce.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: In a retrospective study, we analyzed the outcome of infants who had chronic kidney disease and started RRT within their first year of life. Between 1997 and 2008, all 29 infants who were younger than 1 yr, had end-stage renal failure, and underwent RRT (dialysis or transplantation) at Hannover Medical School were analyzed for up to 12 yr.
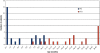
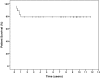
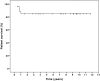
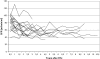
Results: Twenty-seven of 29 infants with chronic kidney disease received peritoneal dialysis, starting at a mean age of 112 d; two children received preemptive renal transplantation (RTx). During follow-up, 21 of 29 children survived with RTx. The 5-yr patient and graft survival rate after RTx was 95.5%. Six of 29 children died, one with a functioning graft and five while on peritoneal dialysis. The main causes of death were severe cardiovascular and cerebral comorbidities. The mean GFR at last follow-up of patients who underwent RTx (mean time after RTx 5.1 yr) was 63.2 ml/min per 1.73 m(2).
Conclusions: RRT in infants who are younger than 1 year offers excellent chances of survival and should be offered to all infants who do not have severe, life-limiting extrarenal comorbidity. Contrary to previous observations, the long-term outcome of infants may be comparable to that of older children who undergo RRT.
Figures
References
-
- Moel DI, Butt KM: Renal transplantation in children less than 2 years of age. J Pediatr 99: 535–539, 1981 - PubMed
-
- Geary DF: Attitudes of pediatric nephrologists to management of end-stage renal disease in infants. J Pediatr 133: 154–156, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Warady BA, Hebert D, Sullivan EK, Alexander SR, Tejani A: Renal transplantation, chronic dialysis, and chronic renal insufficiency in children and adolescents: The 1995 Annual Report of the North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study. Pediatr Nephrol 11: 49–64, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Ehrich JH, Rizzoni G, Brunner FP, Fassbinder W, Geerlings W, Mallick NP, Raine AE, Selwood NH, Tufveson G: Renal replacement therapy for end-stage renal failure before 2 years of age. Nephrol Dial Transplant 7: 1171–1177, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Offner G, Hoyer PF, Ehrich JH, Pichlmayr R, Brodehl J: Paediatric aspects of renal transplantation: Experience of a single centre. Eur J Pediatr 151[Suppl 1]: S16–S22, 1992 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

