VLDL lipolysis products increase VLDL fluidity and convert apolipoprotein E4 into a more expanded conformation
- PMID: 19965582
- PMCID: PMC3035491
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M000406
VLDL lipolysis products increase VLDL fluidity and convert apolipoprotein E4 into a more expanded conformation
Abstract
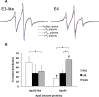
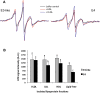
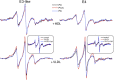
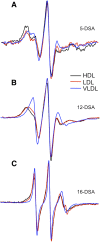
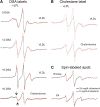
Our previous work indicated that apolipoprotein (apo) E4 assumes a more expanded conformation in the postprandial period. The postprandial state is characterized by increased VLDL lipolysis. In this article, we tested the hypothesis that VLDL lipolysis products increase VLDL particle fluidity, which mediates expansion of apoE4 on the VLDL particle. Plasma from healthy subjects was collected before and after a moderately high-fat meal and incubated with nitroxyl-spin labeled apoE. ApoE conformation was examined by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using targeted spin probes on cysteines introduced in the N-terminal (S76C) and C-terminal (A241C) domains. Further, we synthesized a novel nitroxyl spin-labeled cholesterol analog, which gave insight into lipoprotein particle fluidity. Our data revealed that the order of lipoprotein fluidity was HDL approximately LDL<VLDL<VLDL+lipoprotein lipase. Moreover, the conformation of apoE4 depended on the lipoprotein fraction: VLDL-associated apoE4 had a more linear conformation than apoE4 associated with LDL or HDL. Further, by changing VLDL fluidity, VLDL lipolysis products significantly altered apoE4 into a more expanded conformation. Our studies indicate that after every meal, VLDL fluidity is increased causing apoE4 associated with VLDL to assume a more expanded conformation, potentially enhancing the pathogenicity of apoE4 in vascular tissue.
Figures
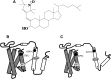

References
-
- Davignon J. 2005. Apolipoprotein E and atherosclerosis: beyond lipid effect. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25: 267–269. - PubMed
-
- Weisgraber K. H. 1990. Apolipoprotein E distribution among human plasma lipoproteins: role of the cysteine-arginine interchange at residue 112. J. Lipid Res. 31: 1503–1511. - PubMed
-
- Wetterau J. R., Aggerbeck L. P., Rall S. C., Jr., Weisgraber K. H. 1988. Human apolipoprotein E3 in aqueous solution. I. Evidence for two structural domains. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 6240–6248. - PubMed
-
- Dong L. M., Weisgraber K. H. 1996. Human apolipoprotein E4 domain interaction. Arginine 61 and glutamic acid 255 interact to direct the preference for very low density lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 19053–19057. - PubMed
-
- Saito H., Dhanasekaran P., Baldwin F., Weisgraber K. H., Phillips M. C., Lund-Katz S. 2003. Effects of polymorphism on the lipid interaction of human apolipoprotein E. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 40723–40729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

