Cholesterol efflux to apoA-I in ABCA1-expressing cells is regulated by Ca2+-dependent calcineurin signaling
- PMID: 19965585
- PMCID: PMC2853441
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M003145
Cholesterol efflux to apoA-I in ABCA1-expressing cells is regulated by Ca2+-dependent calcineurin signaling
Abstract
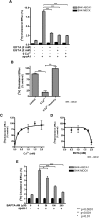
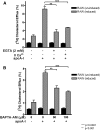
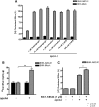
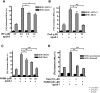
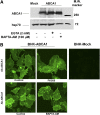
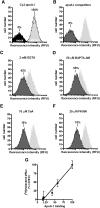
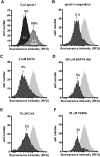
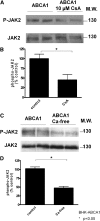
ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) is required for the lipidation of apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I), although molecular mechanisms supporting this process remain poorly defined. In this study, we focused on the role of cytosolic Ca(2+) and its signaling and found that cytosolic Ca(2+) was required for cholesterol efflux to apoA-I. Removing extracellular Ca(2+) or chelating cytosolic Ca(2+) were equally inhibitory for apoA-I lipidation. We provide evidence that apoA-I induced Ca(2+) influx from the medium. We further demonstrate that calcineurin activity, the downstream target of Ca(2+) influx, was essential; inhibition of calcineurin activity by cyclosporine A or FK506 completely abolished apoA-I lipidation. Furthermore, calcineurin inhibition abolished apoA-I binding and diminished JAK2 phosphorylation, an established signaling event for cholesterol efflux to apoA-I. Finally, we demonstrate that neither Ca(2+) manipulation nor calcineurin inhibition influenced ABCA1's capacity to release microparticles or to remodel the plasma membrane. We conclude that this Ca(2+)-dependent calcineurin/JAK2 pathway is specifically responsible for apoA-I lipidation without directly modifying ABCA1 activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The interaction of ApoA-I and ABCA1 triggers signal transduction pathways to mediate efflux of cellular lipids.Mol Med. 2012 Mar 27;18(1):149-58. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00183. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22064972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Janus kinase 2 modulates the apolipoprotein interactions with ABCA1 required for removing cellular cholesterol.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 27;279(9):7622-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312571200. Epub 2003 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14668333
-
ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux generates microparticles in addition to HDL through processes governed by membrane rigidity.J Lipid Res. 2009 Mar;50(3):456-466. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800345-JLR200. Epub 2008 Oct 21. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 18941142
-
ABCA1 increases extracellular ATP to mediate cholesterol efflux to ApoA-I.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Oct;301(4):C886-94. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00042.2011. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21697542
-
ATP-binding cassette transporter AI and its role in HDL formation.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005 Feb;16(1):19-25. doi: 10.1097/00041433-200502000-00005. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005. PMID: 15650559 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidized LDL-bound CD36 recruits an Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase-Lyn complex in macrophages that promotes atherosclerosis.Sci Signal. 2015 Sep 8;8(393):ra91. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa9623. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 26350901 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of ApoA-I and ABCA1 triggers signal transduction pathways to mediate efflux of cellular lipids.Mol Med. 2012 Mar 27;18(1):149-58. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00183. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22064972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xanthine-based KMUP-1 improves HDL via PPARγ/SR-B1, LDL via LDLRs, and HSL via PKA/PKG for hepatic fat loss.J Lipid Res. 2015 Nov;56(11):2070-84. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M057547. Epub 2015 Sep 8. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 26351364 Free PMC article.
-
Microparticles: a critical component in the nexus between inflammation, immunity, and thrombosis.Semin Immunopathol. 2011 Sep;33(5):469-86. doi: 10.1007/s00281-010-0239-3. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Semin Immunopathol. 2011. PMID: 21866419 Review.
-
Tristetraprolin-dependent post-transcriptional regulation of inflammatory cytokine mRNA expression by apolipoprotein A-I: role of ATP-binding membrane cassette transporter A1 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 22;286(16):13834-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.202275. Epub 2011 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21339300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higgins C. F. 2001. ABC transporters: physiology, structure and mechanism–an overview. Res. Microbiol. 152: 205–210. - PubMed
-
- Haidar B., Denis M., Krimbou L., Marcil M., Genest J., Jr 2002. cAMP induces ABCA1 phosphorylation activity and promotes cholesterol efflux from fibroblasts. J. Lipid Res. 43: 2087–2094. - PubMed
-
- Kiss R. S., Maric J., Marcel Y. L. 2005. Lipid efflux in human and mouse macrophagic cells: evidence for differential regulation of phospholipid and cholesterol efflux. J. Lipid Res. 46: 1877–1887. - PubMed
-
- Nofer J. R., Feuerborn R., Levkau B., Sokoll A., Seedorf U., Assmann G. 2003. Involvement of Cdc42 signaling in apoA-I-induced cholesterol efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 53055–53062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

