Liver X receptor activation promotes macrophage-to-feces reverse cholesterol transport in a dyslipidemic hamster model
- PMID: 19965597
- PMCID: PMC2842160
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M001552
Liver X receptor activation promotes macrophage-to-feces reverse cholesterol transport in a dyslipidemic hamster model
Abstract
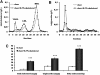
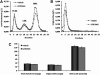
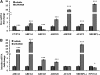
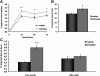
Liver X receptor (LXR) activation promotes reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) in rodents but has major side effects (increased triglycerides and LDL-cholesterol levels) in species expressing cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP). In the face of dyslipidemia, it remains unclear whether LXR activation stimulates RCT in CETP species. We therefore used a hamster model made dyslipidemic with a 0.3% cholesterol diet and treated with vehicle or LXR agonist GW3965 (30 mg/kg bid) over 10 days. To investigate RCT, radiolabeled (3)H-cholesterol macrophages or (3)H-cholesteryl oleate-HDL were then injected to measure plasma and feces radioactivity over 72 or 48 h, respectively. The cholesterol-enriched diet increased VLDL-triglycerides and total cholesterol levels in all lipoprotein fractions and strongly increased liver lipids. Overall, GW3965 failed to improve both dyslipidemia and liver steatosis. However, after (3)H-cholesterol labeled macrophage injection, GW3965 treatment significantly increased the (3)H-tracer appearance by 30% in plasma over 72 h, while fecal (3)H-cholesterol excretion increased by 156% (P < 0.001). After (3)H-cholesteryl oleate-HDL injection, GW3965 increased HDL-derived cholesterol fecal excretion by 64% (P < 0.01 vs. vehicle), while plasma fractional catabolic rate remained unchanged. Despite no beneficial effect on dyslipidemia, LXR activation promotes macrophage-to-feces RCT in dyslipidemic hamsters. These results emphasize the use of species with a more human-like lipoprotein metabolism for drug profiling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anacetrapib and dalcetrapib differentially alters HDL metabolism and macrophage-to-feces reverse cholesterol transport at similar levels of CETP inhibition in hamsters.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 5;740:135-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.06.022. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25008069
-
Upregulating reverse cholesterol transport with cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibition requires combination with the LDL-lowering drug berberine in dyslipidemic hamsters.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Jan;33(1):13-23. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.252932. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23139291
-
Tissue-specific liver X receptor activation promotes macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in vivo.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Apr;30(4):781-6. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.195693. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20110577 Free PMC article.
-
The use of dyslipidemic hamsters to evaluate drug-induced alterations in reverse cholesterol transport.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Mar;11(3):289-97. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20178042 Review.
-
Liver X receptors (LXR) as therapeutic targets in dyslipidemia.Cardiovasc Ther. 2008 Winter;26(4):297-316. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5922.2008.00062.x. Cardiovasc Ther. 2008. PMID: 19035881 Review.
Cited by
-
P2Y13 receptor regulates HDL metabolism and atherosclerosis in vivo.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 25;9(4):e95807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095807. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24769858 Free PMC article.
-
CETP inhibitor torcetrapib promotes reverse cholesterol transport in obese insulin-resistant CETP-ApoB100 transgenic mice.Clin Transl Sci. 2011 Dec;4(6):414-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2011.00344.x. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Clin Transl Sci. 2011. PMID: 22212222 Free PMC article.
-
High-fructose diet downregulates long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 3 expression in liver of hamsters via impairing LXR/RXR signaling pathway.J Lipid Res. 2013 May;54(5):1241-54. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M032599. Epub 2013 Feb 20. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23427282 Free PMC article.
-
Role of liver X receptors in cholesterol efflux and inflammatory signaling (review).Mol Med Rep. 2012 Apr;5(4):895-900. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.758. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Mol Med Rep. 2012. PMID: 22267249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of reverse cholesterol transport - a comprehensive appraisal of available animal studies.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012 Mar 29;9(1):25. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-25. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22458435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fiévet C., Staels B. 2009. Liver X receptor modulators: effects on lipid metabolism and potential use in the treatment of atherosclerosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 77: 1316–1327 - PubMed
-
- Naik S. U., Wang X., Da Silva J. S., Jaye M., Macphee C. H., Reilly M. P., Billheimer J. T., Rothblat G. H., Rader D. J. 2006. Pharmacological activation of liver X receptors promotes reverse cholesterol transport in vivo. Circulation. 113: 90–97 - PubMed
-
- Calpe-Berdiel L., Rotllan N., Fiévet C., Roig R., Blanco-Vaca F., Escolà-Gil J. C. 2008. Liver X receptor-mediated activation of reverse cholesterol transport from macrophages to feces in vivo requires ABCG5/G8. J. Lipid Res. 49: 1904–1911 - PubMed
-
- Repa J. J., Mangelsdorf D. J. 2002. The liver X receptor gene team: potential new players in atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 8: 1243–1248 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

