Diabetes reduces the cholesterol exporter ABCA1 in mouse macrophages and kidneys
- PMID: 19965614
- PMCID: PMC2882721
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M003525
Diabetes reduces the cholesterol exporter ABCA1 in mouse macrophages and kidneys
Abstract
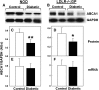
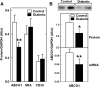
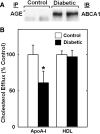
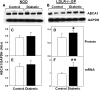
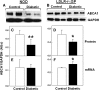
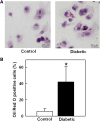
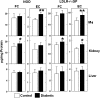
Accumulation of cholesterol in arterial macrophages may contribute to diabetes-accelerated atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCA1 is a cardioprotective membrane protein that mediates cholesterol export from macrophages. Factors elevated in diabetes, such as reactive carbonyls and free fatty acids, destabilize ABCA1 protein in cultured macrophages, raising the possibility that impaired ABCA1 plays an atherogenic role in diabetes. We therefore examined the modulation of ABCA1 in two mouse models of diabetes. We isolated peritoneal macrophages, livers, kidneys, and brains from type 1 non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice and mice made diabetic by viral-induced autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta-cells, and we measured ABCA1 protein and mRNA levels and cholesterol contents. ABCA1 protein levels and cholesterol export activity were reduced by 40-44% (P<0.01) in peritoneal macrophages and protein levels by 48% (P<0.001) in kidneys in diabetic NOD mice compared with nondiabetic animals, even though ABCA1 mRNA levels were not significantly different. A similar selective reduction in ABCA1 protein was found in peritoneal macrophages (33%, P<0.05) and kidneys (35%, P<0.05) from the viral-induced diabetic mice. In liver and brain, however, diabetes had no effect or slightly increased ABCA1 protein and mRNA levels. The reduced ABCA1 in macrophages and kidneys was associated with increased cholesterol content. Impaired ABCA1-mediated cholesterol export could therefore contribute to the increased atherosclerosis and nephropathy associated with diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Oram J. F., Heinecke J. W. 2005. ATP-binding cassette transporter A1: a cell cholesterol exporter that protects against cardiovascular disease. Physiol. Rev. 85: 1343–1372. - PubMed
-
- Singaraja R. R., Brunham L. R., Visscher H., Kastelein J. J., Hayden M. R. 2003. Efflux and atherosclerosis: the clinical and biochemical impact of variations in the ABCA1 gene. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23: 1322–1332. - PubMed
-
- van Eck M., Bos I. S., Kaminski W. E., Orso E., Rothe G., Twisk J., Bottcher A., Van Amersfoort E. S., Christiansen-Weber T. A., Fung-Leung W. P., et al. 2002. Leukocyte ABCA1 controls susceptibility to atherosclerosis and macrophage recruitment into tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99: 6298–6303. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aiello R. J., Brees D., Bourassa P. A., Royer L., Lindsey S., Coskran T., Haghpassand M., Francone O. L. 2002. Increased atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic mice with inactivation of ABCA1 in macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 22: 630–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

