Short-term inhibition of p53 combined with keratinocyte growth factor improves thymic epithelial cell recovery and enhances T-cell reconstitution after murine bone marrow transplantation
- PMID: 19965631
- PMCID: PMC2817635
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-223198
Short-term inhibition of p53 combined with keratinocyte growth factor improves thymic epithelial cell recovery and enhances T-cell reconstitution after murine bone marrow transplantation
Abstract
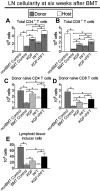
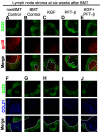
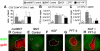
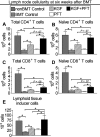
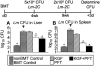
Myeloablative conditioning before bone marrow transplantation (BMT) results in thymic epithelial cell (TEC) injury, T-cell immune deficiency, and susceptibility to opportunistic infections. Conditioning regimen-induced TEC damage directly contributes to slow thymopoietic recovery after BMT. Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) is a TEC mitogen that stimulates proliferation and, when given before conditioning, reduces TEC injury. Some TEC subsets are refractory to KGF and functional T-cell responses are not fully restored in KGF-treated BM transplant recipients. Therefore, we investigated whether the addition of a pharmacologic inhibitor, PFT-beta, to transiently inhibit p53 during radiotherapy could spare TECs from radiation-induced damage in congenic and allogeneic BMTs. Combined before BMT KGF + PFT-beta administration additively restored numbers of cortical and medullary TECs and improved thymic function after BMT, resulting in higher numbers of donor-derived, naive peripheral CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. Radiation conditioning caused a loss of T-cell zone fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) and CCL21 expression in lymphoid stroma. KGF + PFT-beta treatment restored both FRC and CCL21 expression, findings that correlated with improved T-cell reconstitution and an enhanced immune response against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Thus, transient p53 inhibition combined with KGF represents a novel and potentially translatable approach to promote rapid and durable thymic and peripheral T-cell recovery after BMT.
Figures

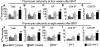
References
-
- Markova M, Barker JN, Miller JS, et al. Fludarabine vs cladribine plus busulfan and low-dose TBI as reduced intensity conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a prospective randomized trial. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007;39(4):193–199. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg K, Blazar BR, Wagner JE, et al. Factors affecting thymic function after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2001;97(5):1458–1466. - PubMed
-
- Douek DC, Vescio RA, Betts MR, et al. Assessment of thymic output in adults after haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation and prediction of T-cell reconstitution. Lancet. 2000;355(9218):1875–1881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

