Retrovirus gene therapy for X-linked chronic granulomatous disease can achieve stable long-term correction of oxidase activity in peripheral blood neutrophils
- PMID: 19965657
- PMCID: PMC2815517
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-222760
Retrovirus gene therapy for X-linked chronic granulomatous disease can achieve stable long-term correction of oxidase activity in peripheral blood neutrophils
Abstract
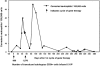
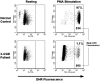
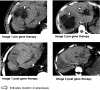
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality from infection. The first CGD gene therapy trial resulted in only short-term marking of 0.01% to 0.1% of neutrophils. A recent study, using busulfan conditioning and an SFFV retrovirus vector, achieved more than 20% marking in 2 patients with X-linked CGD. However, oxidase correction per marked neutrophil was less than normal and not sustained. Despite this, patients clearly benefited in that severe infections resolved. As such, we initiated a gene therapy trial for X-CGD to treat severe infections unresponsive to conventional therapy. We treated 3 adult patients using busulfan conditioning and an MFGS retroviral vector encoding gp91(phox), achieving early marking of 26%, 5%, and 4% of neutrophils, respectively, with sustained long-term marking of 1.1% and 0.03% of neutrophils in 2 of the patients. Gene-marked neutrophils have sustained full correction of oxidase activity for 34 and 11 months, respectively, with full or partial resolution of infection in those 2 patients. Gene marking is polyclonal with no clonal dominance. We conclude that busulfan conditioning together with an MFGS vector is capable of achieving long-term correction of neutrophil oxidase function sufficient to provide benefit in management of severe infection. This study was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT00394316.
Figures

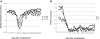
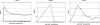

References
-
- Winkelstein JA, Marino MC, Johnston RB, Jr, et al. Chronic granulomatous disease: report on a national registry of 368 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2000;79(3):155–169. - PubMed
-
- Segal BH, Leto TL, Gallin JI, Malech HL, Holland SM. Genetic, biochemical, and clinical features of chronic granulomatous disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 2000;79(3):170–200. - PubMed
-
- Mardiney M, 3rd, Jackson SH, Spratt SK, Li F, Holland SM, Malech HL. Enhanced host defense after gene transfer in the murine p47phox-deficient model of chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1997;89(7):2268–2275. - PubMed
-
- Dinauer MC, Li LL, Bjorgvinsdottir H, Ding C, Pech N. Long-term correction of phagocyte NADPH oxidase activity by retroviral-mediated gene transfer in murine X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1999;94(3):914–922. - PubMed
-
- Sokolic RA, Sekhsaria S, Sugimoto Y, et al. A bicistronic retrovirus vector containing a picornavirus internal ribosome entry site allows for correction of X-linked CGD by selection for MDR1 expression. Blood. 1996;87(1):42–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

