Vascular endothelial growth factor activation of endothelial cells is mediated by early growth response-3
- PMID: 19965691
- PMCID: PMC2845904
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-233478
Vascular endothelial growth factor activation of endothelial cells is mediated by early growth response-3
Abstract
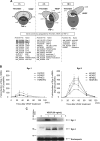
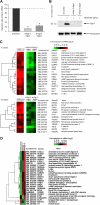
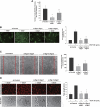
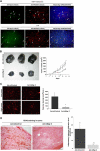
Endothelial cell activation and dysfunction underlie many vascular disorders, including atherosclerosis, tumor growth, and sepsis. Endothelial cell activation, in turn, is mediated primarily at the level of gene transcription. Here, we show that in response to several activation agonists, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and thrombin, endothelial cells demonstrate rapid and profound induction of the early growth response (Egr) genes egr-1 and egr-3. In VEGF-treated endothelial cells, induction of Egr-3 was far greater and more prolonged compared with Egr-1. VEGF-mediated stimulation of Egr-3 involved the inducible binding of NFATc, serum response factor, and CREB to their respective consensus motifs in the upstream promoter region of Egr-3. Knockdown of Egr-3 markedly impaired VEGF-mediated proliferation, migration, and tube formation of endothelial cells and blocked VEGF-induced monocyte adhesion. Egr-3 knockdown abrogated VEGF-mediated vascular outgrowth from ex vivo aortic rings and attenuated Matrigel plug vascularization and melanoma tumor growth in vivo. Together, these findings suggest that Egr-3 is a critical determinant of VEGF signaling in activated endothelial cells. Thus, Egr-3 represents a potential therapeutic target in VEGF-mediated vasculopathic diseases.
Figures



Comment in
-
Wake-up call for endothelial cells.Blood. 2010 Mar 25;115(12):2336-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-256933. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20339106 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide approaches reveal functional vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-inducible nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) c1 binding to angiogenesis-related genes in the endothelium.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 17;289(42):29044-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.555235. Epub 2014 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25157100 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor of activated T cells and early growth response-1 cooperate to mediate tissue factor gene induction by vascular endothelial growth factor in endothelial cells.Thromb Haemost. 2007 Jun;97(6):988-97. doi: 10.1160/th07-01-0037. Thromb Haemost. 2007. PMID: 17549302 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor- and thrombin-induced termination factor, Down syndrome critical region-1, attenuates endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 26;279(48):50537-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406454200. Epub 2004 Sep 23. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15448146
-
Signals and genes induced by angiogenic growth factors in comparison to inflammatory cytokines in endothelial cells.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2007;37(1-2):57-62. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2007. PMID: 17641395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Growth Response-1, an Integrative Sensor in Cardiovascular and Inflammatory Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Nov 16;10(22):e023539. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.023539. Epub 2021 Nov 10. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34755520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of NFAT in the Progression of Diabetic Atherosclerosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Mar 11;8:635172. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.635172. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33791348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opposing role for Egr3 in nucleus accumbens cell subtypes in cocaine action.J Neurosci. 2015 May 20;35(20):7927-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0548-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25995477 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Role for Egr3 in Nucleus Accumbens D2-Medium Spiny Neurons Following Long-Term Abstinence From Cocaine Self-administration.Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 1;87(11):992-1000. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.10.019. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31858986 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Inducible Factors (HIF1α and HIF3α) are differentially methylated in preeclampsia placentae and are associated with birth outcomes.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Oct;478(10):2309-2318. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04661-y. Epub 2023 Jan 28. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36708442
-
Multifaceted regulatory mechanisms of the EGR family in tumours and prospects for therapeutic applications (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jul;56(1):113. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5554. Epub 2025 May 30. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40444475 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Minami T, Aird WC. Endothelial cell gene regulation. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2005;15(5):174–184. - PubMed
-
- Milbrandt J. A nerve growth factor-induced gene encodes a possible transcriptional regulatory factor. Science. 1987;238(4828):797–799. - PubMed
-
- Forsdyke DR. cDNA cloning of mRNAS which increase rapidly in human lymphocytes cultured with concanavalin-A and cycloheximide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985;129(3):619–625. - PubMed
-
- Sukhatme VP, Kartha S, Toback FG, Taub R, Hoover RG, Tsai-Morris CH. A novel early growth response gene rapidly induced by fibroblast, epithelial cell and lymphocyte mitogens. Oncogene Res. 1987;1(4):343–355. - PubMed
-
- Patwardhan S, Gashler A, Siegel MG, et al. EGR3, a novel member of the Egr family of genes encoding immediate-early transcription factors. Oncogene. 1991;6(6):917–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

