Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic hepatitis C virus infection
- PMID: 19965718
- PMCID: PMC3436126
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1178178
Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic hepatitis C virus infection
Abstract
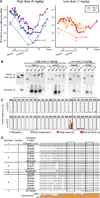
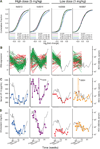
The liver-expressed microRNA-122 (miR-122) is essential for hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA accumulation in cultured liver cells, but its potential as a target for antiviral intervention has not been assessed. We found that treatment of chronically infected chimpanzees with a locked nucleic acid (LNA)-modified oligonucleotide (SPC3649) complementary to miR-122 leads to long-lasting suppression of HCV viremia, with no evidence of viral resistance or side effects in the treated animals. Furthermore, transcriptome and histological analyses of liver biopsies demonstrated derepression of target mRNAs with miR-122 seed sites, down-regulation of interferon-regulated genes, and improvement of HCV-induced liver pathology. The prolonged virological response to SPC3649 treatment without HCV rebound holds promise of a new antiviral therapy with a high barrier to resistance.
Figures
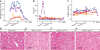
Comment in
-
Antagonizing microRNA-122 and treatment of hepatitis C virus infection.Hepatology. 2010 Apr;51(4):1461-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.23573. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20373371 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

