Hierarchy of lesion processing governs the repair, double-strand break formation and mutability of three-lesion clustered DNA damage
- PMID: 19965771
- PMCID: PMC2831305
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1070
Hierarchy of lesion processing governs the repair, double-strand break formation and mutability of three-lesion clustered DNA damage
Abstract
Ionising radiation induces clustered DNA damage sites which pose a severe challenge to the cell's repair machinery, particularly base excision repair. To date, most studies have focussed on two-lesion clusters. We have designed synthetic oligonucleotides to give a variety of three-lesion clusters containing abasic sites and 8-oxo-7, 8-dihydroguanine to investigate if the hierarchy of lesion processing dictates whether the cluster is cytotoxic or mutagenic. Clusters containing two tandem 8-oxoG lesions opposing an AP site showed retardation of repair of the AP site with nuclear extract and an elevated mutation frequency after transformation into wild-type or mutY Escherichia coli. Clusters containing bistranded AP sites with a vicinal 8-oxoG form DSBs with nuclear extract, as confirmed in vivo by transformation into wild-type E. coli. Using ung1 E. coli, we propose that DSBs arise via lesion processing rather than stalled replication in cycling cells. This study provides evidence that it is not only the prompt formation of DSBs that has implications on cell survival but also the conversion of non-DSB clusters into DSBs during processing and attempted repair. The inaccurate repair of such clusters has biological significance due to the ultimate risk of tumourigenesis or as potential cytotoxic lesions in tumour cells.
Figures

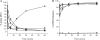
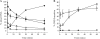
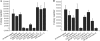
References
-
- Frelon S, Douki T, Cadet J. Radical oxidation of the adenine moiety of nucleoside and DNA: 2-hydroxy-2′-deoxyadenosine is a minor decomposition product. Free Radic. Res. 2002;36:499–508. - PubMed
-
- Pouget JP, Frelon S, Ravanat JL, Testard I, Odin F, Cadet J. Formation of modified DNA bases in cells exposed either to gamma radiation or to high-LET particles. Radiat. Res. 2002;157:589–595. - PubMed
-
- Ward JF. DNA damage produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: identities, mechanisms of formation, and reparability. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1988;35:95–125. - PubMed
-
- von Sonntag C. Free-Radical-Induced DNA Damage and Its Repair. Springer, Verlag: Heidelberg; 2006.

