The 5A apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide displays antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 19965776
- PMCID: PMC2828392
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.200196
The 5A apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide displays antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
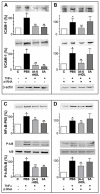
Objective: The apolipoprotein (apo)A-I mimetic peptide 5A is highly specific for ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC)A1-mediated cholesterol efflux. We investigated whether the 5A peptide shares other beneficial features of apoA-I, such as protection against inflammation and oxidation. Methods- New Zealand white rabbits received an infusion of apoA-I, reconstituted high-density lipoprotein (HDL) containing apoA-I ([A-I]rHDL), or the 5A peptide complexed with phospholipids (1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine [PLPC]), before inserting a collar around the carotid artery. Human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) were incubated with (A-I)rHDL or 5A/PLPC before stimulation with tumor necrosis factor alpha. Results- ApoA-I, (A-I)rHDL, and 5A/PLPC reduced the collar-mediated increase in (1) endothelial expression of cell adhesion molecules vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1; (2) production, as well as the expression of the Nox4 catalytic subunits of the NADPH oxidase; and (3) infiltration of circulating neutrophils into the carotid intima-media. In HCAECs, both 5A/PLPC and (A-I)rHDL inhibited tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression, as well as the nuclear factor kappaB signaling cascade and production. The effects of the 5A/PLPC complex were no longer apparent in HCAECs knocked down for ABCA1.
Conclusions: Like apoA-I, the 5A peptide inhibits acute inflammation and oxidative stress in rabbit carotids and HCAECs. In vitro, the 5A peptide exerts these beneficial effects through interaction with ABCA1.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide ETC-642 exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that are comparable to high density lipoproteins.Atherosclerosis. 2011 Aug;217(2):395-400. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.04.001. Epub 2011 Apr 16. Atherosclerosis. 2011. PMID: 21571275
-
Nonenzymatic glycation impairs the antiinflammatory properties of apolipoprotein A-I.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Apr;30(4):766-72. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.201715. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20110571 Free PMC article.
-
The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, ETC-642, reduces chronic vascular inflammation in the rabbit.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Nov 30;10:224. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-224. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22128776 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Vascular Inflammation by Apolipoprotein A-IV.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 30;9:901408. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.901408. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35845068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloperoxidase: an inflammatory enzyme for generating dysfunctional high density lipoprotein.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2006 Jul;21(4):322-8. doi: 10.1097/01.hco.0000231402.87232.aa. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16755201 Review.
Cited by
-
HDL, Atherosclerosis, and Emerging Therapies.Cholesterol. 2013;2013:891403. doi: 10.1155/2013/891403. Epub 2013 May 28. Cholesterol. 2013. PMID: 23781332 Free PMC article.
-
High-density lipoproteins are a potential therapeutic target for age-related macular degeneration.J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 25;295(39):13601-13616. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.012305. Epub 2020 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32737203 Free PMC article.
-
New kids on the block: the emerging role of apolipoproteins in the pathogenesis and treatment of asthma.Chest. 2011 Oct;140(4):1048-1054. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-0158. Chest. 2011. PMID: 21972383 Free PMC article.
-
Intriguing bronchoalveolar lavage proteome in a case of pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis.Am J Case Rep. 2013 Apr 29;14:129-33. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.889037. Print 2013. Am J Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23875058 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Functions of High-Density Lipoprotein in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 28;13(1):57. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010057. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38247481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lewis GF, Rader DJ. New insights into the regulation of HDL metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport. Circ Res. 2005;96:1221–1232. - PubMed
-
- Tabet F, Rye KA. High-density lipoproteins, inflammation and oxidative stress. Clin Sci (Lond) 2009;116:87–98. - PubMed
-
- Nicholls SJ, Dusting GJ, Cutri B, Bao S, Drummond GR, Rye KA, Barter PJ. Reconstituted high-density lipoproteins inhibit the acute pro-oxidant and proinflammatory vascular changes induced by a periarterial collar in normocholesterolemic rabbits. Circulation. 2005;111:1543–1550. - PubMed
-
- Forte TM, Oda MN, Knoff L, Frei B, Suh J, Harmony JA, Stuart WD, Rubin EM, Ng DS. Targeted disruption of the murine lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase gene is associated with reductions in plasma paraoxonase and platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase activities but not in apolipoprotein J concentration. J Lipid Res. 1999;40:1276–1283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

