Stimulation of sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling as an alveolar cell survival strategy in emphysema
- PMID: 19965812
- PMCID: PMC5455841
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200906-0826OC
Stimulation of sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling as an alveolar cell survival strategy in emphysema
Abstract
Rationale: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibition increases ceramides in lung structural cells of the alveolus, initiating apoptosis and alveolar destruction morphologically resembling emphysema. The effects of increased endogenous ceramides could be offset by sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), a prosurvival by-product of ceramide metabolism.
Objectives: The aims of our work were to investigate the sphingosine-S1P-S1P receptor axis in the VEGFR inhibition model of emphysema and to determine whether stimulation of S1P signaling is sufficient to functionally antagonize alveolar space enlargement.
Methods: Concurrent to VEGFR blockade in mice, S1P signaling augmentation was achieved via treatment with the S1P precursor sphingosine, S1P agonist FTY720, or S1P receptor-1 (S1PR1) agonist SEW2871. Outcomes included sphingosine kinase-1 RNA expression and activity, sphingolipid measurements by combined liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, immunoblotting for prosurvival signaling pathways, caspase-3 activity and terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assays, and airspace morphometry.
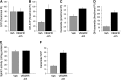
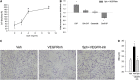
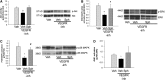
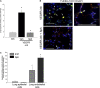
Measurements and main results: Consistent with previously reported de novo activation of ceramide synthesis, VEGFR inhibition triggered increases in lung ceramides, dihydroceramides, and dihydrosphingosine, but did not alter sphingosine kinase activity or S1P levels. Administration of sphingosine decreased the ceramide-to-S1P ratio in the lung and inhibited alveolar space enlargement, along with activation of prosurvival signaling pathways and decreased lung parenchyma cell apoptosis. Sphingosine significantly opposed ceramide-induced apoptosis in cultured lung endothelial cells, but not epithelial cells. FTY720 or SEW2871 recapitulated the protective effects of sphingosine on airspace enlargement concomitant with attenuation of VEGFR inhibitor-induced lung apoptosis.
Conclusions: Strategies aimed at augmenting the S1P-S1PR1 signaling may be effective in ameliorating the apoptotic mechanisms of emphysema development.
Figures
References
-
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The definition of emphysema: report of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Division of Lung Diseases Workshop. Am Rev Respir Dis 1985;132:182–185. - PubMed
-
- Tuder RM, Petrache I, Elias JA, Voelkel NF, Henson PM. Apoptosis and emphysema: the missing link. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2003;28:551–554. - PubMed
-
- Aoshiba K, Yokohori N, Nagai A. Alveolar wall apoptosis causes lung destruction and emphysematous changes. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2003;28:555–562. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

