ERRgamma regulates cardiac, gastric, and renal potassium homeostasis
- PMID: 19965931
- PMCID: PMC2817599
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0114
ERRgamma regulates cardiac, gastric, and renal potassium homeostasis
Abstract
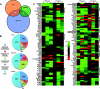
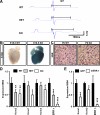
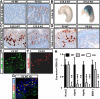
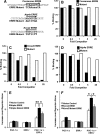
Energy production by oxidative metabolism in kidney, stomach, and heart, is primarily expended in establishing ion gradients to drive renal electrolyte homeostasis, gastric acid secretion, and cardiac muscle contraction, respectively. In addition to orchestrating transcriptional control of oxidative metabolism, the orphan nuclear receptor, estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma), coordinates expression of genes central to ion homeostasis in oxidative tissues. Renal, gastric, and cardiac tissues subjected to genomic analysis of expression in perinatal ERRgamma null mice revealed a characteristic dysregulation of genes involved in transport processes, exemplified by the voltage-gated potassium channel, Kcne2. Consistently, ERRgamma null animals die during the first 72 h of life with elevated serum potassium, reductions in key gastric acid production markers, and cardiac arrhythmia with prolonged QT intervals. In addition, we find altered expression of several genes associated with hypertension in ERRgamma null mice. These findings suggest a potential role for genetic polymorphisms at the ERRgamma locus and ERRgamma modulators in the etiology and treatment of renal, gastric, and cardiac dysfunction.
Figures
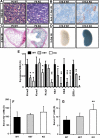
References
-
- Shimkets RA, Warnock DG, Bositis CM, Nelson-Williams C, Hansson JH, Schambelan M, Gill Jr JR, Ulick S, Milora RV, Findling JW, Canessa CM, Rossier BC, Lifton RP 1994 Liddle's syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell 79:407–414 - PubMed
-
- Wang Q, Shen J, Splawski I, Atkinson D, Li Z, Robinson JL, Moss AJ, Towbin JA, Keating MT 1995 SCN5A mutations associated with an inherited cardiac arrhythmia, long QT syndrome. Cell 80:805–811 - PubMed
-
- Splawski I, Timothy KW, Sharpe LM, Decher N, Kumar P, Bloise R, Napolitano C, Schwartz PJ, Joseph RM, Condouris K, Tager-Flusberg H, Priori SG, Sanguinetti MC, Keating MT 2004 Ca(V)1.2 calcium channel dysfunction causes a multisystem disorder including arrhythmia and autism. Cell 119:19–31 - PubMed
-
- Lloyd SE, Pearce SH, Fisher SE, Steinmeyer K, Schwappach B, Scheinman SJ, Harding B, Bolino A, Devoto M, Goodyer P, Rigden SP, Wrong O, Jentsch TJ, Craig IW, Thakker RV 1996 A common molecular basis for three inherited kidney stone diseases. Nature 379:445–449 - PubMed
-
- Bernard G, Shevell MI 2008 Channelopathies: a review. Pediatr Neurol 38:73–85 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

