Tracing cationic nutrients from xylem into stem tissue of French bean by stable isotope tracers and cryo-secondary ion mass spectrometry
- PMID: 19965970
- PMCID: PMC2815875
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.143776
Tracing cationic nutrients from xylem into stem tissue of French bean by stable isotope tracers and cryo-secondary ion mass spectrometry
Abstract
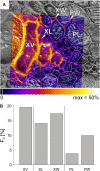
Fluxes of mineral nutrients in the xylem are strongly influenced by interactions with the surrounding stem tissues and are probably regulated by them. Toward a mechanistic understanding of these interactions, we applied stable isotope tracers of magnesium, potassium, and calcium continuously to the transpiration stream of cut bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) shoots to study their radial exchange at the cell and tissue level with stem tissues between pith and phloem. For isotope localization, we combined sample preparation with secondary ion mass spectrometry in a completely cryogenic workflow. After 20 min of application, tracers were readily detectable to various degrees in all tissues. The xylem parenchyma near the vessels exchanged freely with the vessels, its nutrient elements reaching a steady state of strong exchange with elements in the vessels within 20 min, mainly via apoplastic pathways. A slow exchange between vessels and cambium and phloem suggested that they are separated from the xylem, parenchyma, and pith, possibly by an apoplastic barrier to diffusion for nutrients (as for carbohydrates). There was little difference in these distributions when tracers were applied directly to intact xylem via a microcapillary, suggesting that xylem tension had little effect on radial exchange of these nutrients and that their movement was mainly diffusive.
Figures
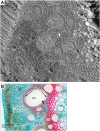
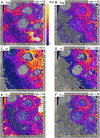
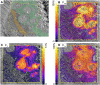
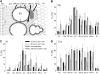
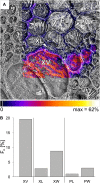
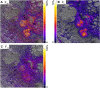
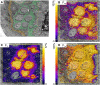
References
-
- Benkert R, Balling A, Zimmermann U (1991) Direct measurement of the pressure and flow in the xylem vessels of Nicotiana tabacum and their dependence on flow resistance and transpiration rate. Bot Acta 104 423–432
-
- Biddulph O, Markle J (1944) Translocation of radiophosphorus in the phloem of the cotton plant. Am J Bot 31 65–70
-
- Black JR, Epstein E, Rains WD, Yin QZ, Casey WH (2008) Magnesium-isotope fractionation during plant growth. Environ Sci Technol 42 7831–7836 - PubMed
-
- Böhlke JK, de Laeter JR, De Bievre P, Hidaka H, Peiser HS, Rosman KJR, Taylor PDP (2005) Isotopic compositions of the elements, 2001. J Phys Chem Ref Data 34 57–67
-
- Gilmer F, Schurr U (2007) Dynamic and nutrient fluxes in the xylem. In B Sattelmacher, WJ Horst, eds, The Apoplast of Higher Plants: Compartment of Storage, Transport, and Reactions. Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 221–229
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

